Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2014; 20(45): 17049-17064
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049
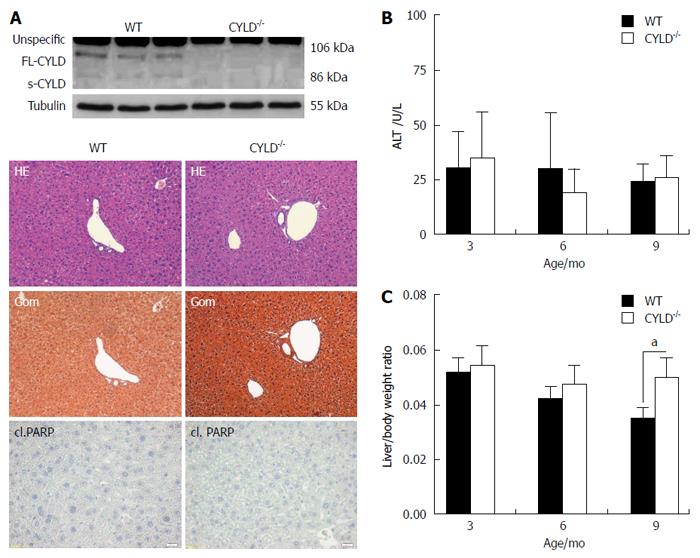
Figure 1 Liver phenotype of CYLD-/- mice.
A: Western blot analysis of liver lysates for CYLD expression (upper panel). Liver histology was unremarkable in both WT and CYLD-/- mice (9 mo old). Spontaneous apoptosis was not detected by cl. PARP immunohistology (Scale bar: 100 μm, lower panel); B: Alanine aminotransferase serum concentration of WT and CYLD-/- mice; C: Liver/body weight ratio of WT and CYLD-/- mice. Values are mean ± SD. n = 6 vs 6. aP < 0.05, WT vs CYLD-/-.
- Citation: Urbanik T, Koehler BC, Wolpert L, Elßner C, Scherr AL, Longerich T, Kautz N, Welte S, Hövelmeyer N, Jäger D, Waisman A, Schulze-Bergkamen H. CYLD deletion triggers nuclear factor-κB-signaling and increases cell death resistance in murine hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(45): 17049-17064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i45/17049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049