Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2014; 20(44): 16690-16697
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16690
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16690
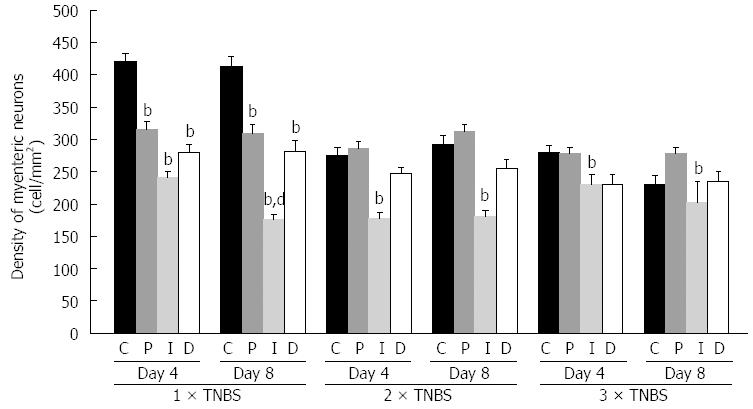
Figure 3 Density of HuC/HuD-immunoreactive myenteric neurons in the colonic segments of control (C) (n = 12) and TNBS-treated rats four (n = 13) and eight (n = 14) days after colitis induction.
In the TNBS-treated groups the inflamed segment (I) and the adjacent proximal (P) and distal (D) colonic segments were examined. Significant decrease in myenteric neuronal density was first detected on day four after each TNBS administration. When the rats were treated only once (1 × TNBS) the number of myenteric neurons decreased significantly in all three colonic segments, while after repeated treatments (2 × TNBS, 3 × TNBS), a significant decrease in neuronal number was demonstrated exclusively in the I segments. After the single dose of TNBS a further significant neuronal loss was detected until day eight post-induction, whereas after repeated treatments the number of myenteric neurons did not decrease further between days four and eight. Data are expressed as means ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs age-matched control groups; dP < 0.01 vs once TNBS-treated group on day four. TNBS: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid.
- Citation: Talapka P, Nagy LI, Pál A, Poles MZ, Berkó A, Bagyánszki M, Puskás LG, Fekete &, Bódi N. Alleviated mucosal and neuronal damage in a rat model of Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(44): 16690-16697
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i44/16690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16690