Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2014; 20(43): 16215-16226
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16215
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16215
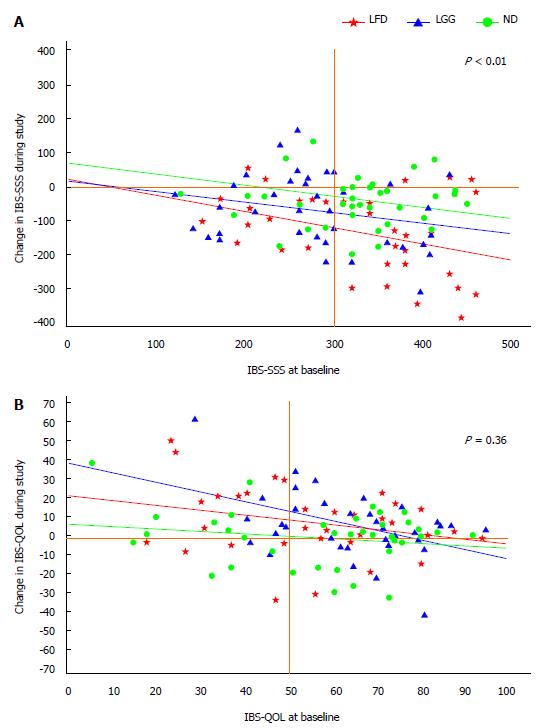
Figure 4 Adjusted linear regression analysis.
A: Changes of irritable bowel syndrome severity score system (IBS-SSS) from baseline toward the end of the study (week 6) in all three groups by baseline covariates, x axis: IBS-SSS at baseline; y axis: Change in IBS-SSS during study; B: Changes of IBS-quality of live (QOL) from baseline toward the end of the study (week 6) in all three groups by baseline covariates. LFD: Low fermentable, oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols diet; LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; ND: Normal (Danish/Western) diet.
-
Citation: Pedersen N, Andersen NN, Végh Z, Jensen L, Ankersen DV, Felding M, Simonsen MH, Burisch J, Munkholm P. Ehealth: Low FODMAP diet
vs Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(43): 16215-16226 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i43/16215.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16215