Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2014; 20(43): 16153-16158
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16153
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16153
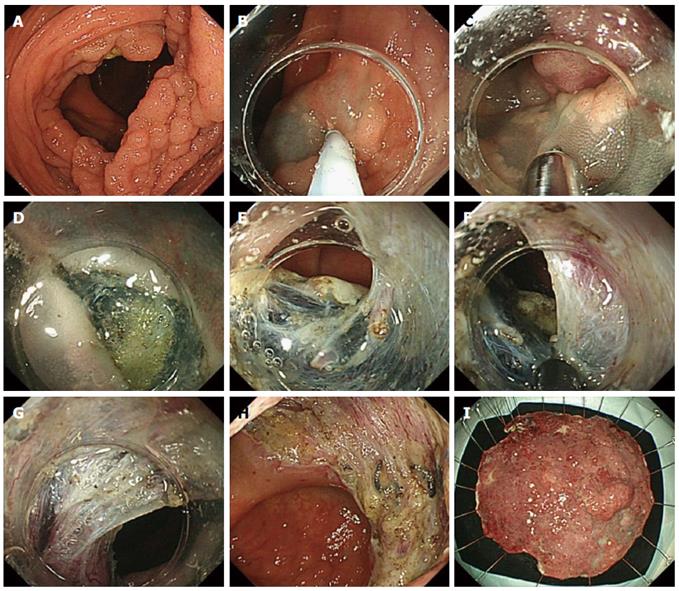
Figure 3 Endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure.
A: A flat elevated lesion (85 mm) located in the ascending colon. It was impossible to have a retroflex view of this lesion; B, C: Submucosal injection of Glyceol and the first circumferential incision were initiated from the oral side of the lesion in the forward view. The first cut was made with the Jet B knife; D: After the first circumferential incision, it was difficult to slide the top of the short-type ST hood into the submucosal layer. The next step was to broaden the visual field by cutting the blue colored submucosal layer near the mucosa carefully (white dotted line); E-G: After step D, it was easy to slide the top of the short-type ST hood into the submucosal layer; it then became easier to cut the submucosal layer. In this situation, the IT knife nano was useful for a quick dissection of the submucosal layer; H, I: En bloc resection was achieved without any adverse events within 180 min.
- Citation: Sakamoto T, Mori G, Yamada M, Kinjo Y, So E, Abe S, Otake Y, Nakajima T, Matsuda T, Saito Y. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasms: A review. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(43): 16153-16158
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i43/16153.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16153