Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2014; 20(43): 16037-16052
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16037
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16037
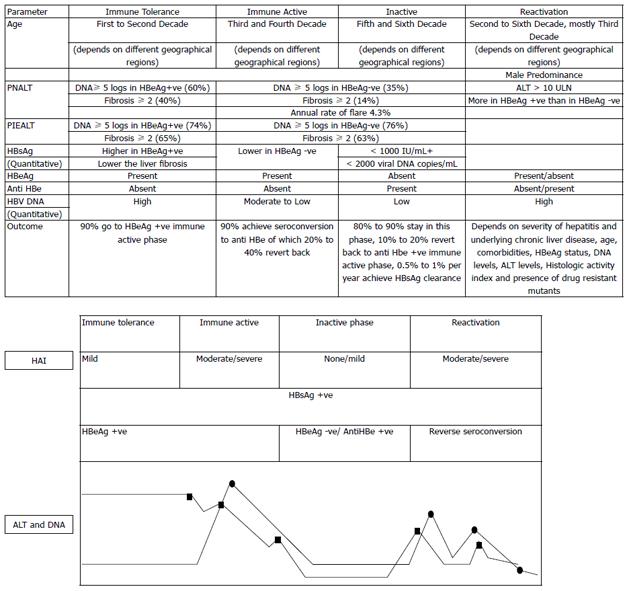
Figure 2 Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and phases of reactivation.
The variations in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and DNA levels are shown in relation to histological activity index (HAI) (also shown in the inset). ALT (circles) and HBV DNA (squares). PIEALT: persistently or intermittently elevated ALT [defined as ≥ 3 ALT values in the year prior to baseline liver biopsy, and all values were > 40 IU/L and had remained so until the start of treatment or last follow-up if not treated (persistently elevated) or if they had ≥ 3 ALT values and ≥ 1 > 40 IU/L in the year prior to baseline biopsy or anytime until the start of treatment or last follow-up, if not treated (intermittently elevated)]. PNALT: Persistently normal ALT (defined as ≥ 3 ALT values in the year prior to baseline liver biopsy, and all values were < 40 IU/L and had remained so until the start of treatment or last follow-up if not treated). HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen.
- Citation: Philips CA, Sarin SK. Potent antiviral therapy improves survival in acute on chronic liver failure due to hepatitis B virus reactivation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(43): 16037-16052
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i43/16037.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16037