Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2014; 20(42): 15787-15796
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15787
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15787
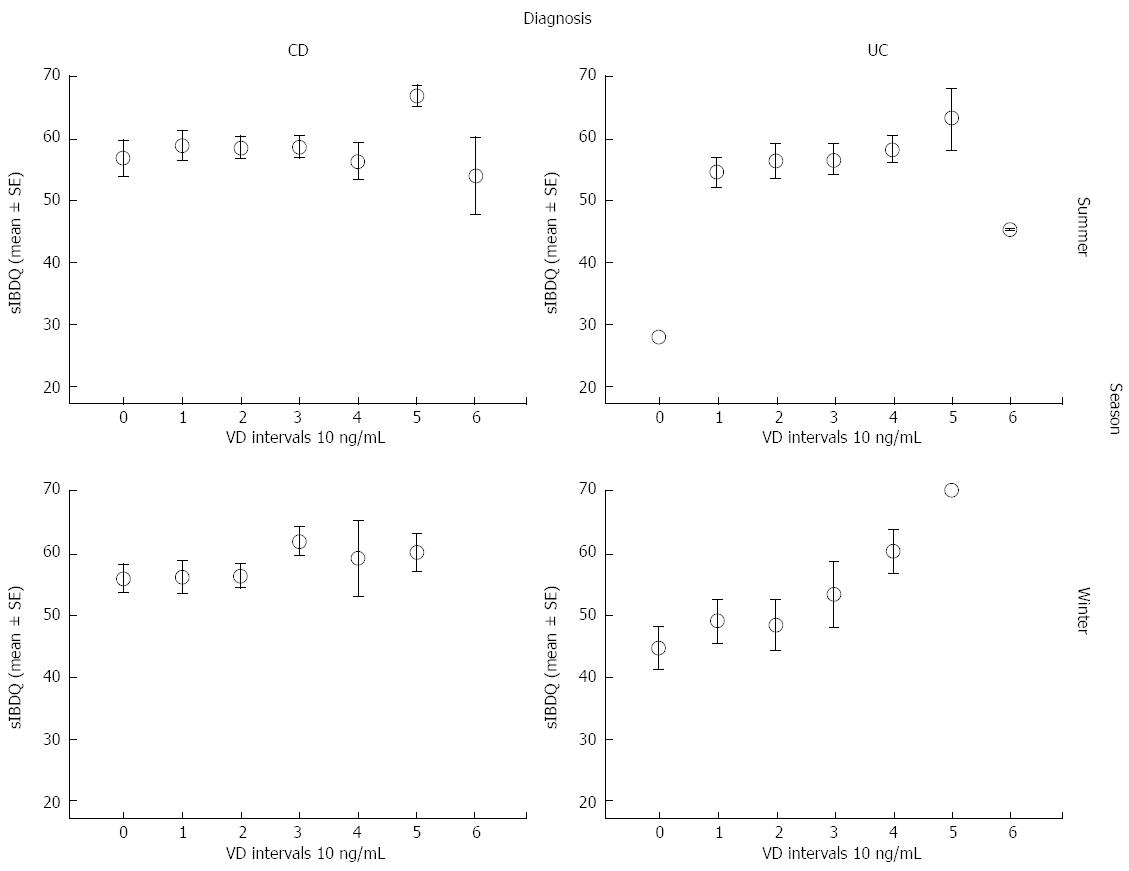
Figure 3 Effect of vitamin D serum concentration on disease activity according to diagnosis and season.
The horizontal lines represent the sIBDQ score mean ± SE. VD serum concentration bins: 0: 0-9.9 ng/mL; 1: 10-19.9 ng/mL; 2: 20-29.9 ng/mL; 3: 30-39.9 ng/mL; 4: 40-49.9 ng/mL; 5: 50-50.9 ng/mL; 6: > 60 ng/mL. VD: Vitamin D; sIBDQ: Short inflammatory bowel diseases questionnaire.
- Citation: Hlavaty T, Krajcovicova A, Koller T, Toth J, Nevidanska M, Huorka M, Payer J. Higher vitamin D serum concentration increases health related quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(42): 15787-15796
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i42/15787.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15787