Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2014; 20(42): 15715-15726
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15715
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15715
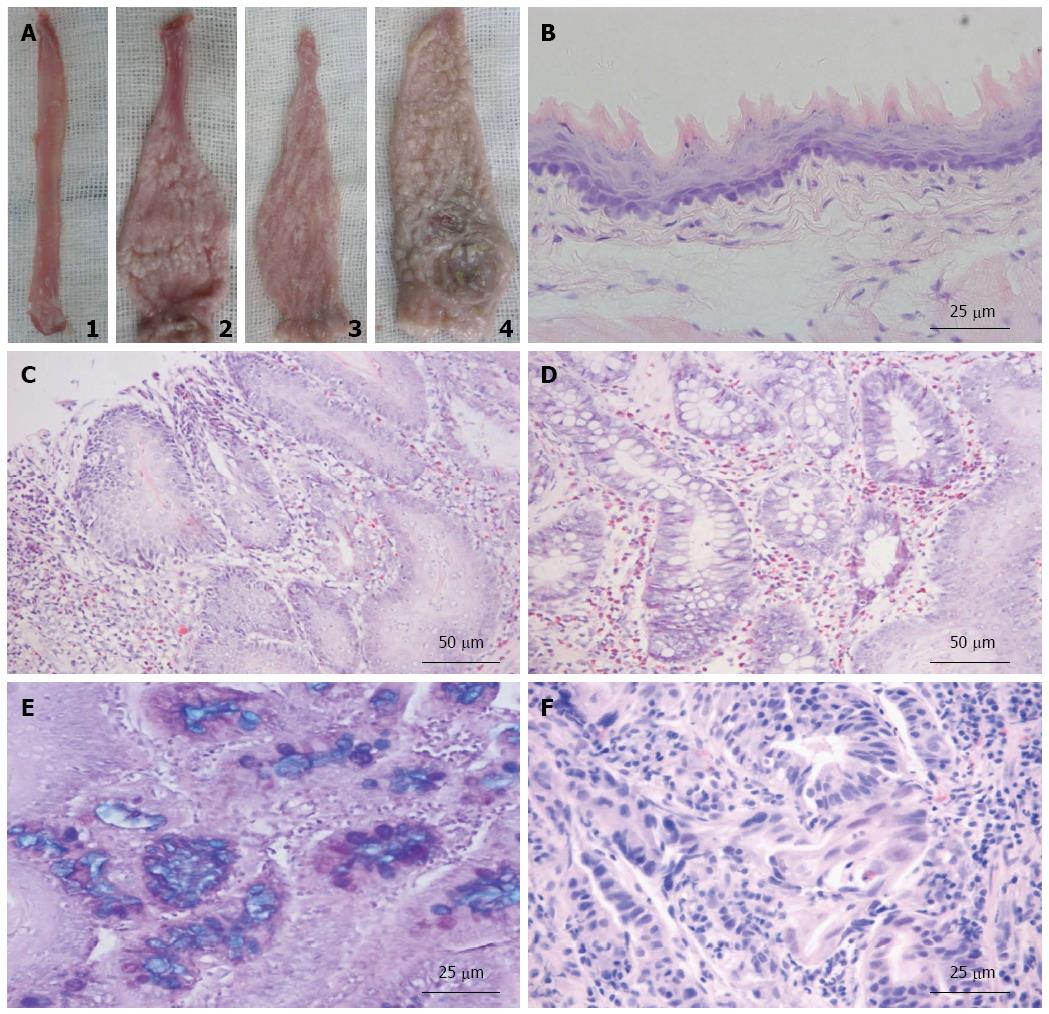
Figure 2 Macroscopic and microscopic findings in the rat esophagus.
A: Macroscopic findings in the esophagus: 1, Normal esophagus; 2, Esophagitis with tree bark appearance; 3, Barrett’s esophagus; and 4, esophageal adenocarcinoma. Microscopic findings; B: Normal squamous epithelium (400 × magnification); C: Reflux esophagitis (200 × magnification); D: Barrett’s esophagus (200 × magnification); E: Intestinal metaplasia in the esophagus detected by High-iron diamine-Alcian Blue-Periodic acid-Schiff (400 × magnification); F: Esophageal adenocarcinoma (400 × magnification).
-
Citation: Chu YX, Wang WH, Dai Y, Teng GG, Wang SJ. Esophageal
Helicobacter pylori colonization aggravates esophageal injury caused by reflux. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(42): 15715-15726 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i42/15715.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15715