Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2014; 20(42): 15703-15714
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15703
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15703
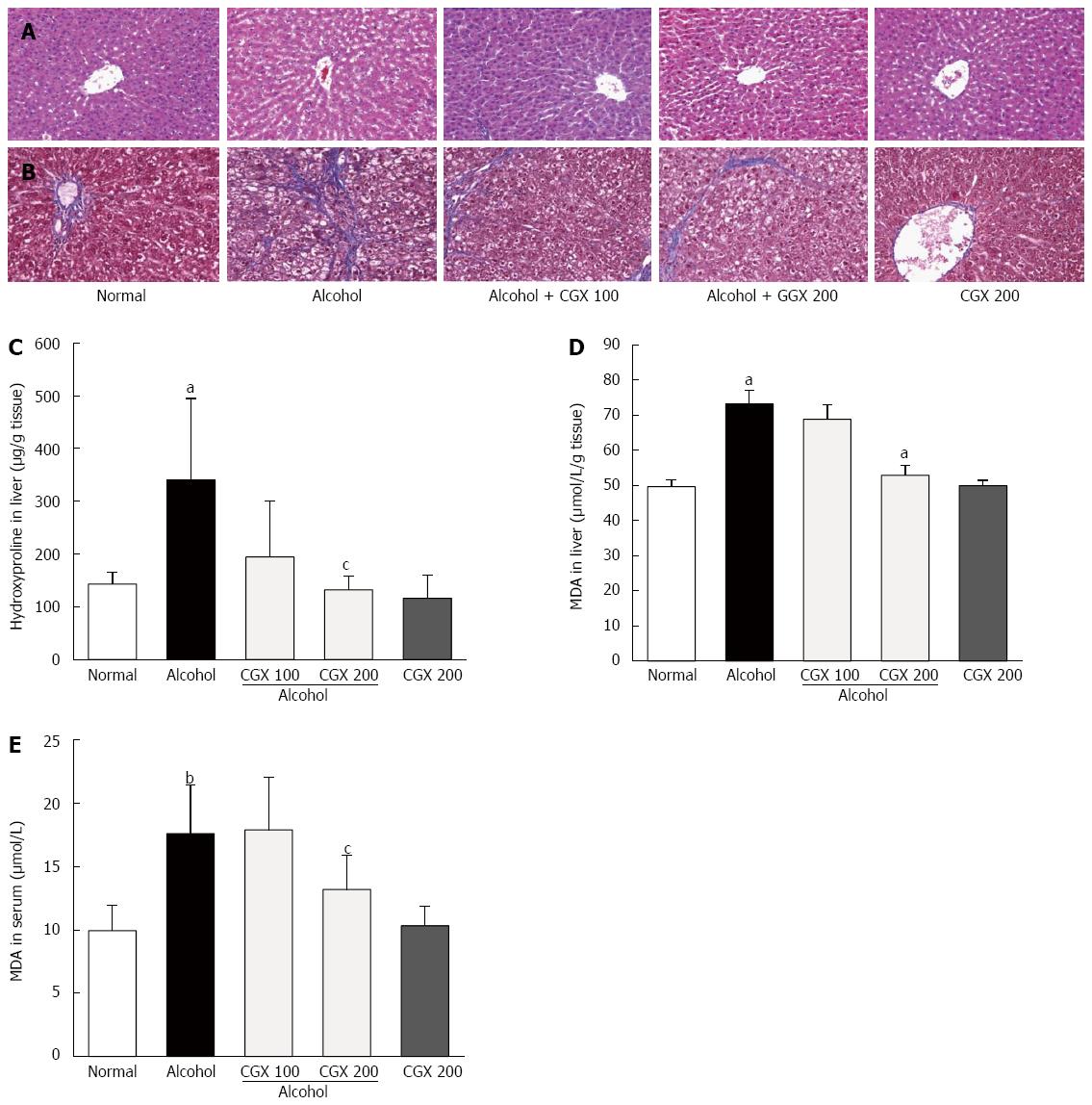
Figure 2 Histopathological examinations and contents of hydroxyproline and malondialdehyde.
Rats were orally administered 30% alcohol (10 mL/kg) with or without Chunggan extract (CGX; 100 or 200 mg/kg) for 4 wk. The removed liver tissues were examined using haematoxylin and eosin (A) and Masson’s trichrome (B) staining under an optical microscope (× 200 magnifications). Hydroxyproline (C) and malondialdehyde (MDA) (D) contents in the liver tissue and serum MDA concentrations (E) were measured. Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 6-9). aP < 0.05 vs normal group, bP < 0.01 vs normal group, cP < 0.05 vs control group.
- Citation: Kim HG, Kim JM, Han JM, Lee JS, Choi MK, Lee DS, Park YH, Son CG. Chunggan extract, a traditional herbal formula, ameliorated alcohol-induced hepatic injury in rat model. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(42): 15703-15714
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i42/15703.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15703