Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2014; 20(42): 15499-15517
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15499
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15499
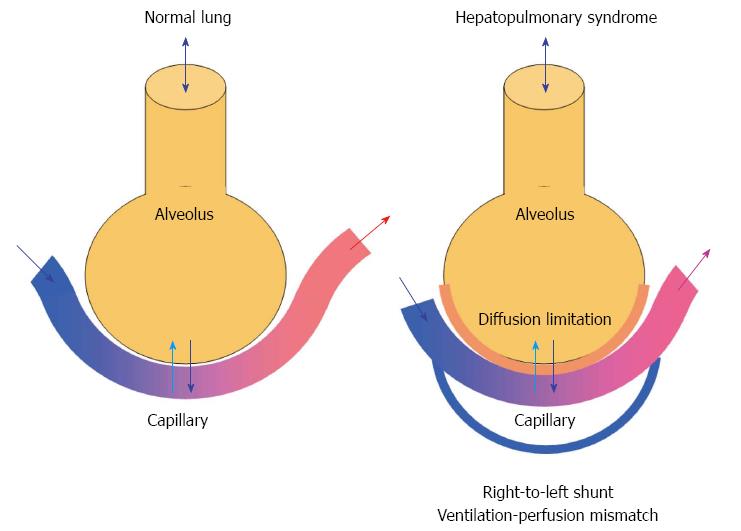
Figure 5 Gas exchange in the normal lung (left) and mechanism of hepatopulmonary syndrome (right).
The hepatopulmonary syndrome comprises an increased alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient owing to diffusion limitations and development of intrapulmonary right-to-left shunts leading to arterial hypoxaemia.
- Citation: Møller S, Henriksen JH, Bendtsen F. Extrahepatic complications to cirrhosis and portal hypertension: Haemodynamic and homeostatic aspects. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(42): 15499-15517
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i42/15499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15499