Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2014; 20(41): 15275-15288
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15275
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15275
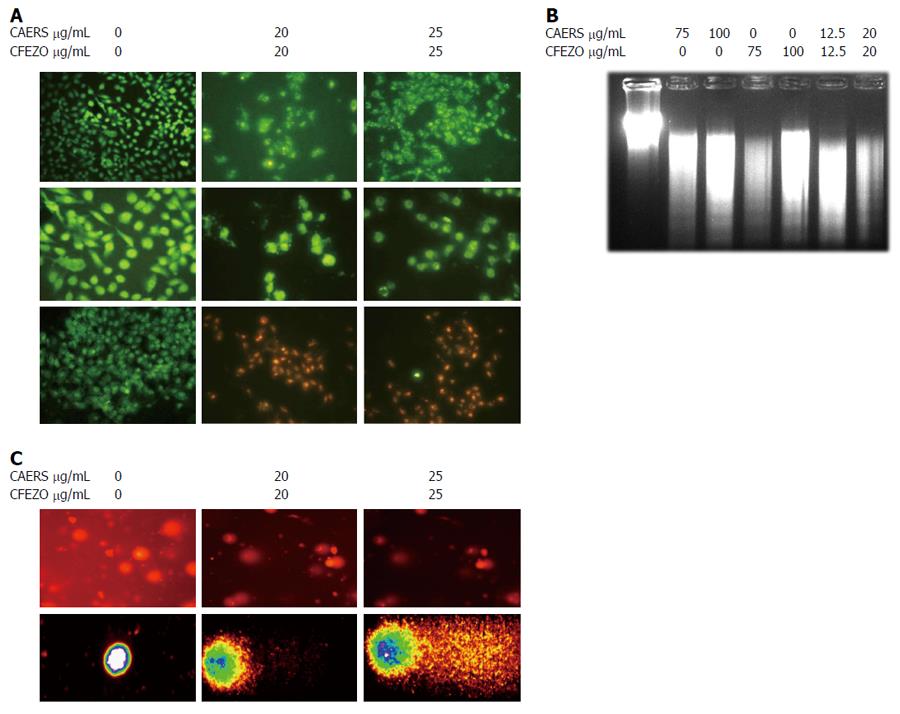
Figure 3 Combination of crude alkaloid and flavonoid induce biochemical features of apoptosis.
HCT116 cells were treated for 24 h with indicated concentrations of crude alkaloid extract of R. stricta (CAERS) and/or crude flavonoid extract of Z. officinale (CFEZO) and assayed for existence of apoptotic cell death. A: Fluorescent images from Hoechst 33342 staining (first and second rows) or acridine orange/ethidium bromide (third row) (arrows indicate nuclear condensation, DNA fragmentation, and perinuclear apoptotic bodies) (magnification: first row: × 20; second and third rows: × 40); B: Agarose gel showing DNA fragmentation in HCT116 cells; C: Comet assay showing formation of DNA tail in CAERS and CFEZO-treated HCT116 cells. Nuclei with damaged DNA have the appearance of a Comet with a bright head and a tail, whereas nuclei with undamaged DNA appear round with no tail.
-
Citation: Elkady AI, Hussein RAEH, Abu-Zinadah OA. Differential control of growth, apoptotic activity and gene expression in human colon cancer cells by extracts derived from medicinal herbs,
Rhazya stricta andZingiber officinale and their combination. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(41): 15275-15288 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i41/15275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15275