Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2014; 20(41): 15087-15097
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15087
Published online Nov 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15087
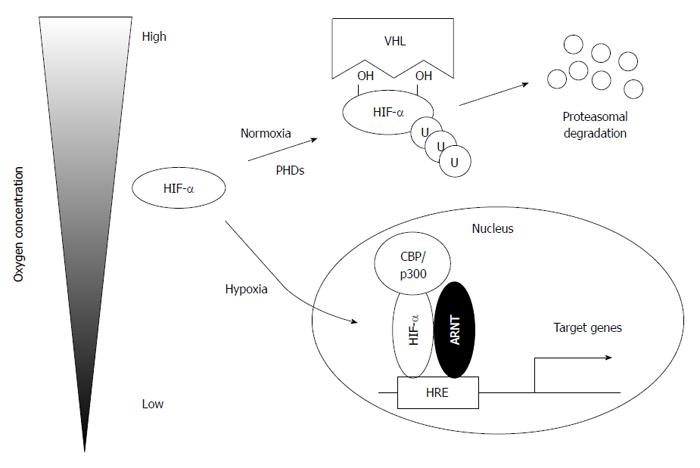
Figure 1 Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors under normal and low oxygen concentrations.
Under normoxia conditions, hypoxia-inducible factor α (HIF-α) is hydroxylated at specific proline residues in an oxygen-dependent manner, ubiquitylated by von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein (pVHL), and, subsequently, degraded by the proteasome. Under hypoxia conditions, stabilized HIF-α translocates to the nucleus and binds aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) to activate its target genes. PHD: Prolyl hydroxylase domain; HRE: Hypoxia-response element.
- Citation: Suzuki T, Shinjo S, Arai T, Kanai M, Goda N. Hypoxia and fatty liver. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(41): 15087-15097
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i41/15087.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15087