Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14895-14903
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14895
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14895
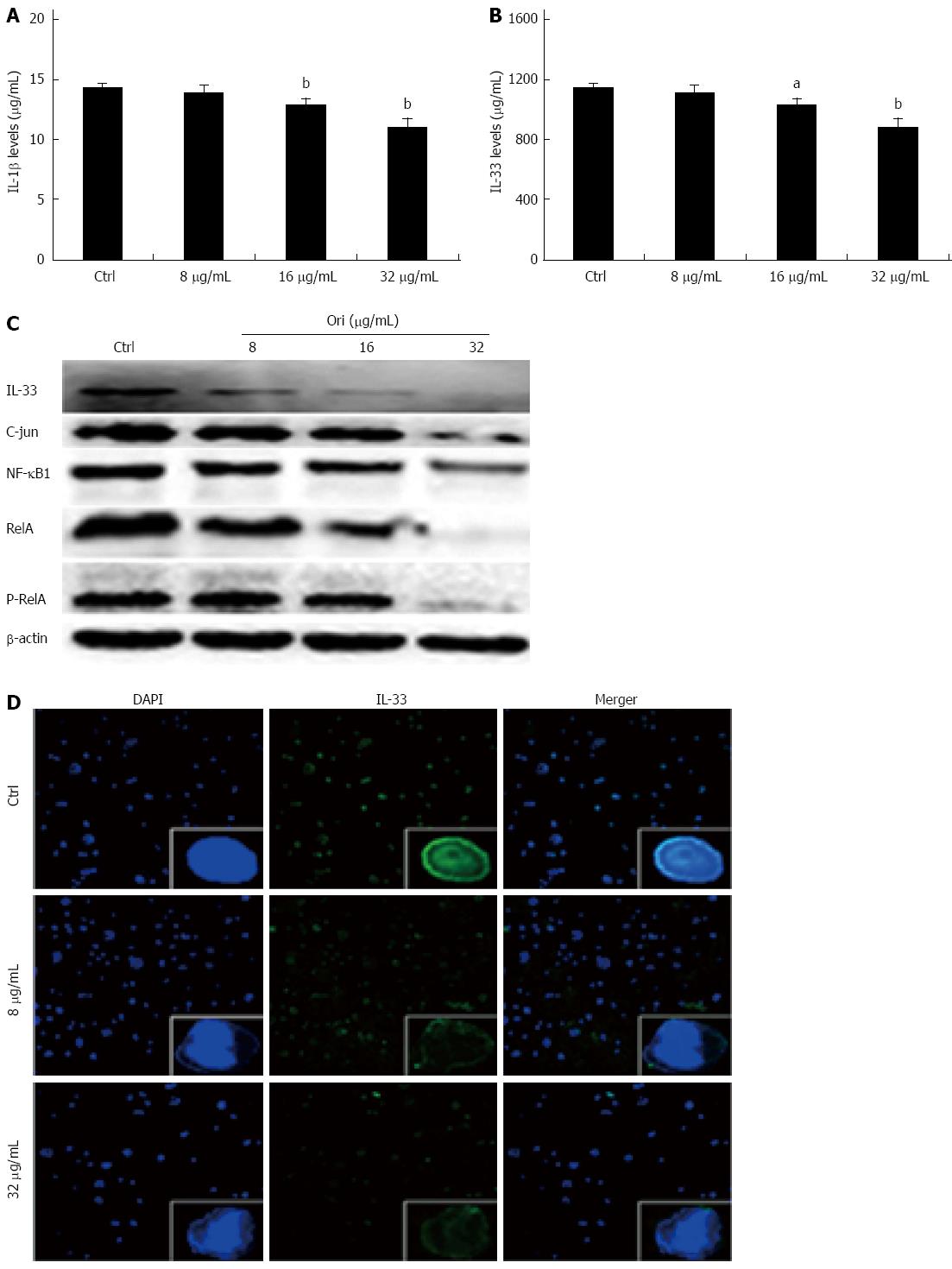
Figure 2 Oridonin decreases both the expression of the nuclear factors nuclear factor κB/activating protein-1/interleukin-33 in BxPC-3 cells and the release of interleukin-1β and interleukin-33 into the supernatant.
A and B: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis of the effect of oridonin on interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-33 in BxPC-3 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the control treatment; C: Western blot analysis of the effect of oridonin on the levels of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and phospho-STAT3 in BxPC-3 cells treated with 0, 8, 16, or 32 μg/mL oridonin for 24 h. Three independent experiments were performed, and a representative result is shown; D: Immunofluorescent staining analysis of the effect of oridonin on IL-33 in BxPC-3 cells (× 100). The BxPC-3 cells were treated with 0, 8, or 32 μg/mL oridonin for 24 h. NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB.
- Citation: Chen RY, Xu B, Chen SF, Chen SS, Zhang T, Ren J, Xu J. Effect of oridonin-mediated hallmark changes on inflammatory pathways in human pancreatic cancer (BxPC-3) cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14895-14903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14895