Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14865-14874
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14865
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14865
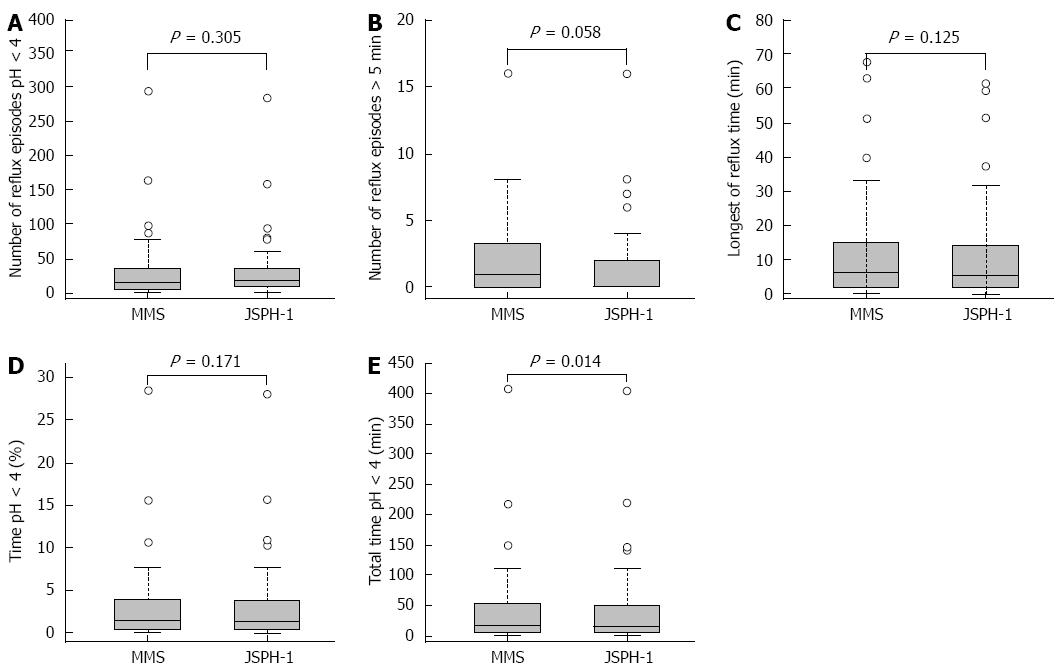
Figure 4 Comparison of esophageal acid exposure measured during 24 h of simultaneous recordings in 45 patients with the conventional pH measurement system and the pH capsule (JSPH-1).
A-D: There were no significant differences in pH parameters including the number of reflux episodes with a pH < 4 (P = 0.305), the number of episodes longer than 5 min (P = 0.058), the longest reflux time (P = 0.125), or the percentage of total time with a pH < 4 (P = 0.171) between the 2 systems; E: Overall median value of the total time with a pH < 4 was significantly shorter with the capsule system than with the catheter system (P = 0.014).
- Citation: Yang XJ, Gan T, Wang L, Liao Z, Tao XH, Shen W, Zhao XY. Wireless esophageal pH capsule for patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A multicenter clinical study. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14865-14874
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14865.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14865