Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14855-14864
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14855
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14855
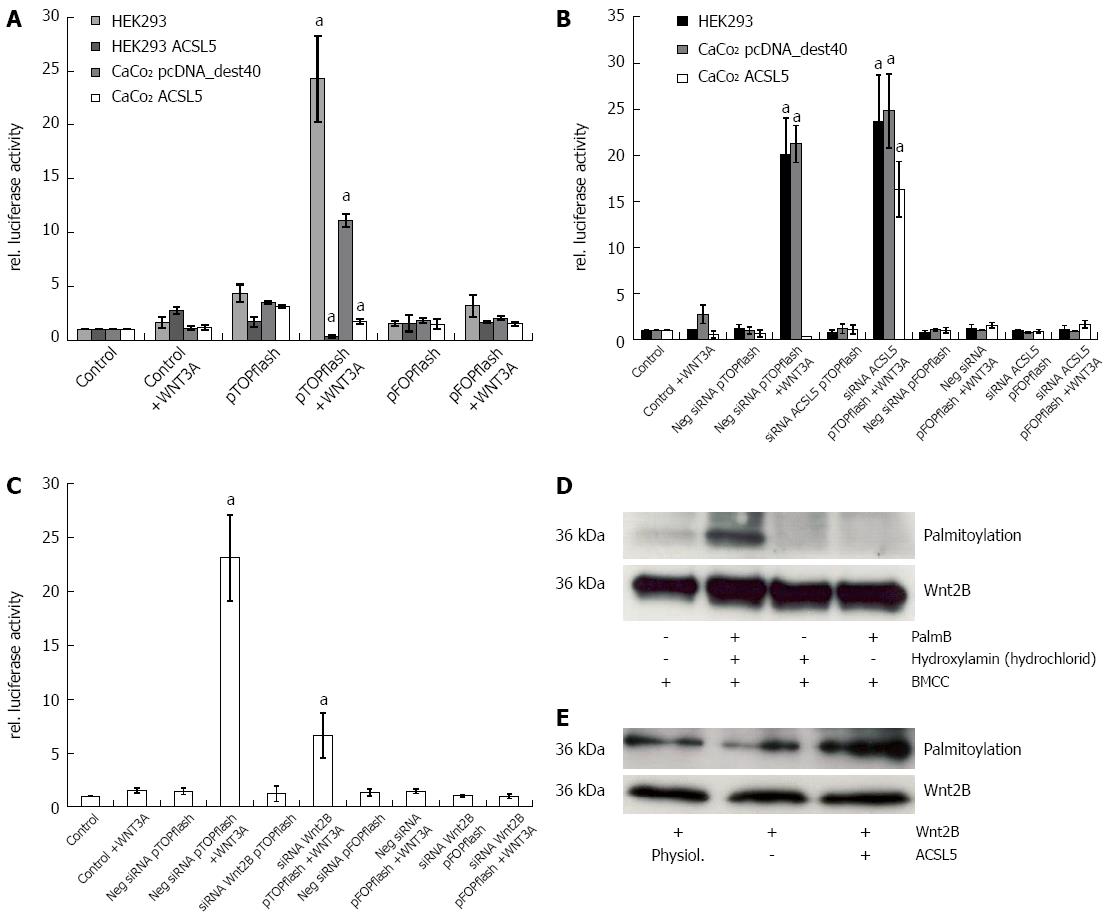
Figure 2 Wnt activation dependent on acyl-CoA synthetase 5 expression.
A: Luciferase reporter assay in HEK293 and CaCo2 cells stably or transiently transfected with acyl-CoA synthetase 5 (ACSL5) and transiently transfected with pTOPflash or pFOPflash. After activation with Wnt3A, Tcf reporter-derived luciferase activity was detected luminometric; B: Luciferase reporter assay after knockdown of ACSL5 by siRNA in HEK293 and CaCo2 cells; C: Luciferase reporter assay after knockdown of Wnt2B by siRNA in HEK293 cells; D: Palmitoylation of Wnt2B dependent on ACSL5 expression. Isolated mitochondria from HEK293 cells, transiently transfected and immunoprecipitated with Wnt2B, with or without treatment with palmostatin B, Hydroxylamine (hydrochloride), and BMCC. As a reference, Wnt2B protein expression was determined; E: Isolated mitochondria from CaCo2 cells, transiently transfected with Wnt2B and ACSL5, immunoprecipitated with Wnt2B, after treatment with palmostatin B, hydroxylamine (hydrochloride), and BMCC. aP < 0.05 vs control.
- Citation: Klaus C, Schneider U, Hedberg C, Schütz AK, Bernhagen J, Waldmann H, Gassler N, Kaemmerer E. Modulating effects of acyl-CoA synthetase 5-derived mitochondrial Wnt2B palmitoylation on intestinal Wnt activity. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14855-14864
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14855.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14855