Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14760-14777
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14760
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14760
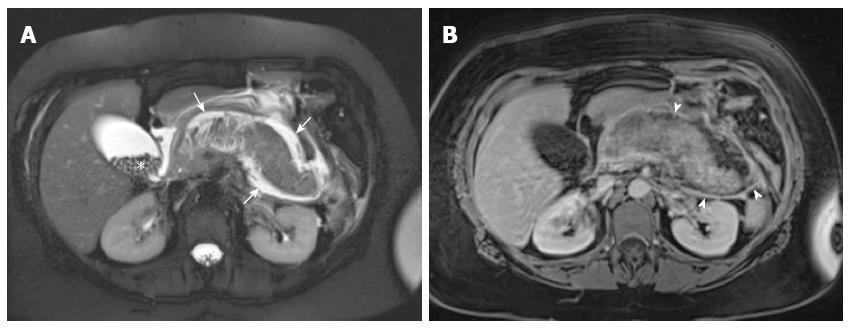
Figure 8 Gallstone acute edematous pancreatitis with acute peripancreatic fluid collection.
A: Axial single-shot turbo spin-echo T2-weighted (HASTE) image with fat-suppression; B: Axial post-Gadolinium 3D-GRE T1-weighted image with fat-suppression. There is diffuse lace-like increased T2 signal involving the pancreatic parenchyma (A), minimally reduced enhancement post-Gadolinium, peripancreatic stranding, and thick rim of enhancement (arrowheads) surrounding the pancreas (B), associated with peripancreatic fluid collection (arrows) in keeping with diffuse edematous pancreatitis and peripancreatic acute peripancreatic fluid collection. There are also innumerable gallstones (asterisk) (A).
- Citation: Manikkavasakar S, AlObaidy M, Busireddy KK, Ramalho M, Nilmini V, Alagiyawanna M, Semelka RC. Magnetic resonance imaging of pancreatitis: An update. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14760-14777
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14760.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14760