Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14706-14716
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14706
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14706
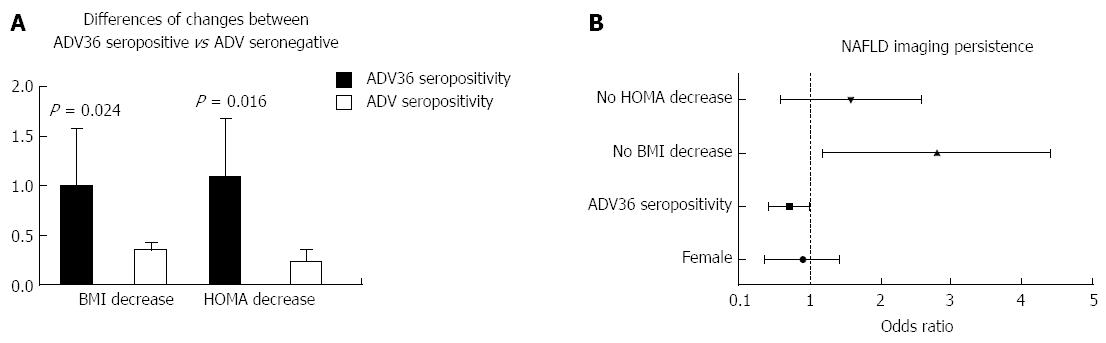
Figure 6 After a comprehensive nutritional and lifestyle intervention, the improvement is more relevant in ADV36 seropositive than in ADV36 seronegative non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a greater decrease of insulin resistance (homeostasis model assessment) and of overweight (body mass index) was achieved in ADV seropositive non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients (A) and the odds of bright liver persistence is associated with lack of insulin resistance (homeostasis model assessment) and body weight (body mass index) decrease, while a relevant association with improvement, i.
e., bright liver disappearance, is observed in ADV36 seropositive non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients (B). BMI: Body mass index; HOMA: Homeostasis model assessment; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Trovato FM, Catalano D, Garozzo A, Martines GF, Pirri C, Trovato GM. ADV36 adipogenic adenovirus in human liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14706-14716
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14706.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14706