Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14706-14716
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14706
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14706
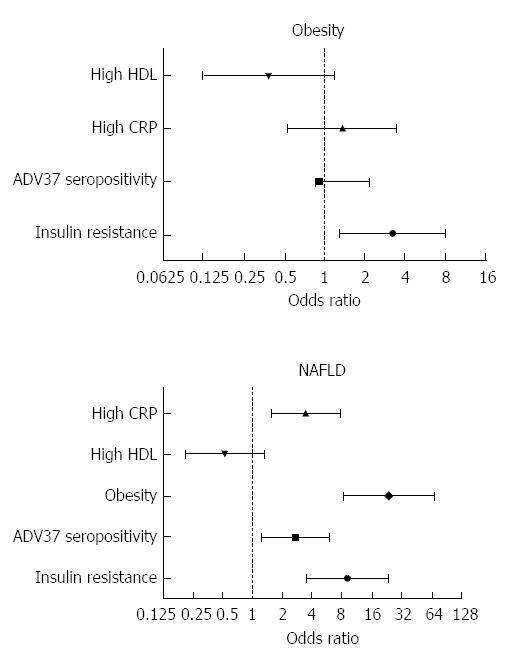
Figure 5 Odds ratio.
Increased risk of obesity (top) is associated with greater insulin resistance, C-reactive protein, and ADV37 seropositivity (Ad37+), whereas higher high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is associated with lower prevalence of obesity. A more consistent association of ADV37+, greater insulin resistance, C-reactive protein (CRP), and obesity was observed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (bottom), whereas higher high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol was associated with a lower prevalence of NAFLD. No sex difference was found. This behavior is different, if not opposite, of that of ADV36.
- Citation: Trovato FM, Catalano D, Garozzo A, Martines GF, Pirri C, Trovato GM. ADV36 adipogenic adenovirus in human liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14706-14716
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14706.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14706