Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14696-14705
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14696
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14696
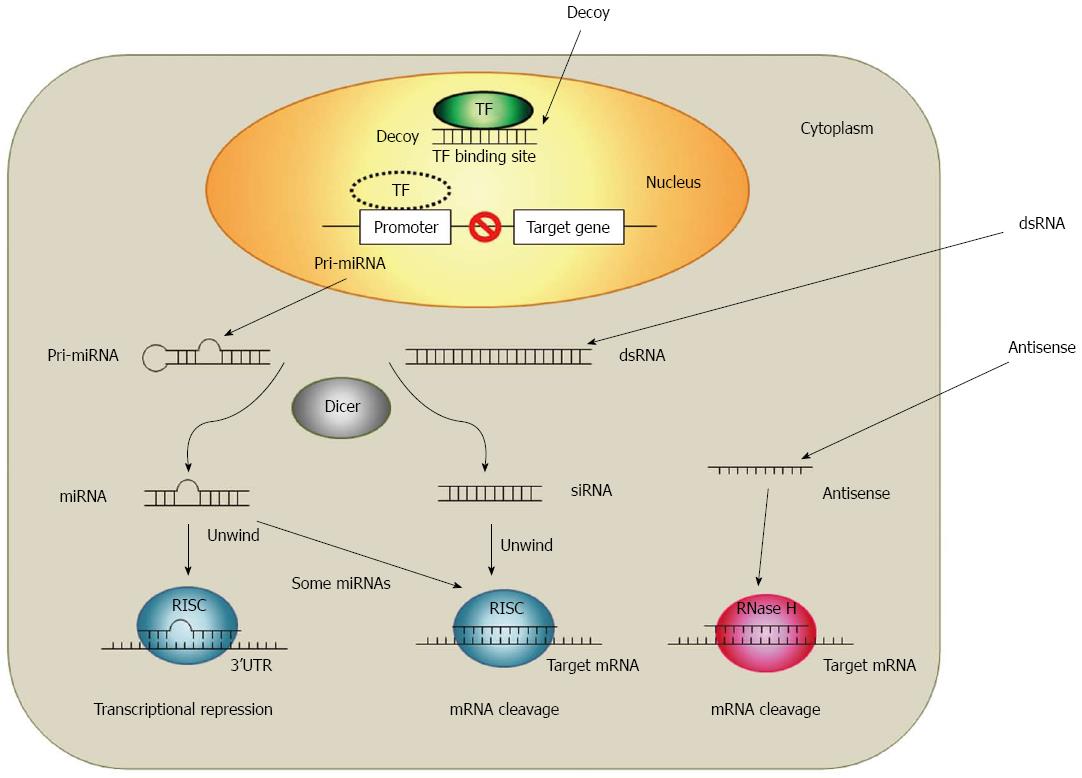
Figure 1 Overview of small RNA and DNA-based therapeutic strategies.
Decoy ODNs block the binding of TF and inhibits specific gene expression at the transcriptional level. MiRNAs are generated in the nucleus (pri-miRNA) and bind to the target 3’ untranslated region (UTR) through imperfect complementarity at multiple sites, which act to its target by translational repression or mRNA cleavage. siRNAs form a perfect duplex with their target mRNA site, which leads to a specific cleavage of target mRNA. Antisense ODNs specifically hybridize with their target mRNA, which activates RNase H-cleavage of the target mRNA. ODNs: Oligodeoxynucleotides; RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; miRNA: Micro RNA; RNase H: Ribonuclease H; dsRNA: Double stranded RNA; TF: Transcription factor; 3’UTR: 3’-untranslated region.
- Citation: Kim KH, Park KK. Small RNA- and DNA-based gene therapy for the treatment of liver cirrhosis, where we are? World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14696-14705
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14696.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14696