Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14672-14685
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14672
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14672
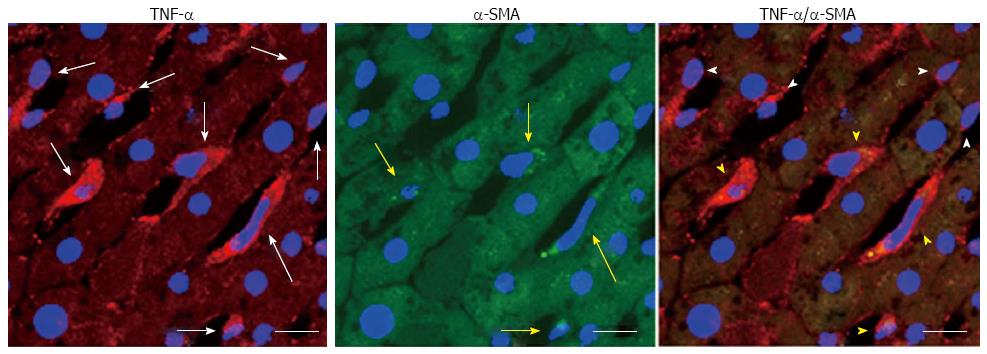
Figure 4 Ethanol-activated hepatic stellate cells, which can product tumor necrosis factor-α in rats fed with a 7-wk 5 g/dL ethanol liquid diet.
The white arrows indicate tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α positive cells; yellow arrows indicate cells positive for α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), a marker of activated hepatic stellate cells; white arrowheads indicate TNF-α positive cells that did not overlap with α-SMA positive cells; yellow arrowheads indicate cells that are both TNF-α- and α-SMA-positive; scale bar = 10 μm.
- Citation: Liu J. Ethanol and liver: Recent insights into the mechanisms of ethanol-induced fatty liver. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14672-14685
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14672.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14672