Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14626-14641
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14626
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14626
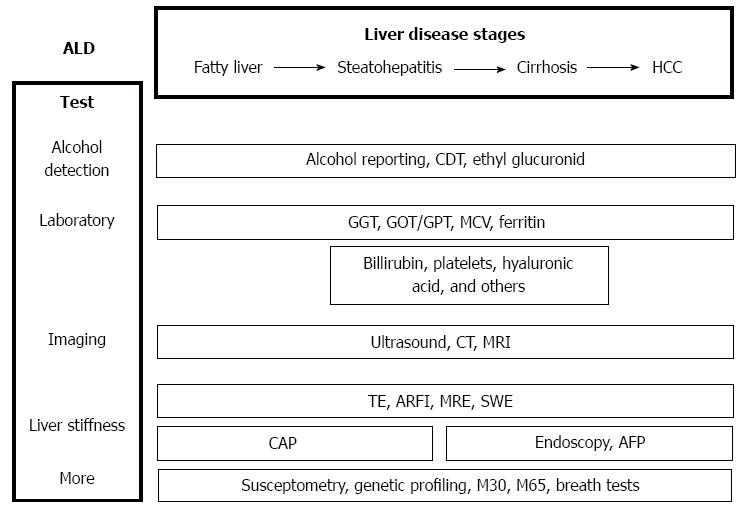
Figure 2 General non-invasive approaches for patients with suspected alcoholic liver disease.
Combination of different tests will help to establish alcohol as underlying reason and to assess the stage of liver disease. ALD: Alcoholic liver disease; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; CDT: Carbohydrate deficient transferrin; MCV: Mean corpuscular volume; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; TE: Transient elastography; ARFI: Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging elastography (Siemens); CAP: Controlled attenuation parameter (Echosens); MRE: Magnetic resonance elastography; SWE: Shear wave elastography (Supersonic imaging); GGT: γ-glutamyl transpeptadase; GOT: Glutamic-oxal(o)acetic transaminase; GPT: Glutamate pyruvate transaminase; AFP: α-fetoprotein.
- Citation: Mueller S, Seitz HK, Rausch V. Non-invasive diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14626-14641
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14626.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14626