Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2014; 20(4): 1030-1037
Published online Jan 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i4.1030
Published online Jan 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i4.1030
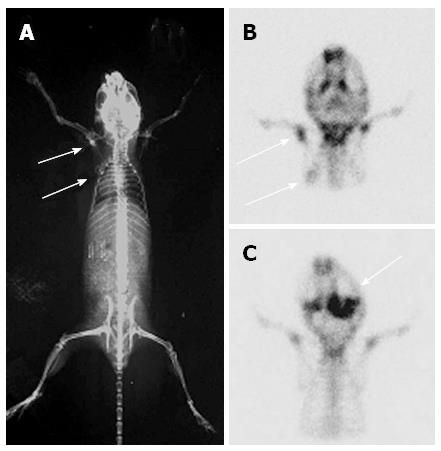
Figure 4 Whole-body X-ray and micro-pinhole bone scintigraphy images of experimental bone metastasis in mice.
A: X-ray image, upper arrow indicates the hot spot of the left humeral osteoblastic metastatic lesion, and the lower arrow indicates the cold spot of the left scapular osteolytic metastatic lesion and circle around the osteogenic reaction; B: Micro-pinhole bone scintigraphy images of the same mouse in the POST position. The osteoblastic metastatic lesion (upper arrow) showed greater accumulation of 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate (99mTc-MDP), and the osteolytic lesion (lower arrow) combined with osteogenic reaction showed less; C: The arrow indicates a mandibular lesion in another mouse with accumulation of 99mTc-MDP.
- Citation: Zhao BZ, Cao J, Shao JC, Sun YB, Fan LM, Wu CY, Liang S, Guo BF, Yang G, Xie WH, Yang QC, Yang SF. Novel esophageal squamous cell carcinoma bone metastatic clone isolated by scintigraphy, X ray and micro PET/CT. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(4): 1030-1037
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i4/1030.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i4.1030