Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2014; 20(39): 14430-14441
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14430
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14430
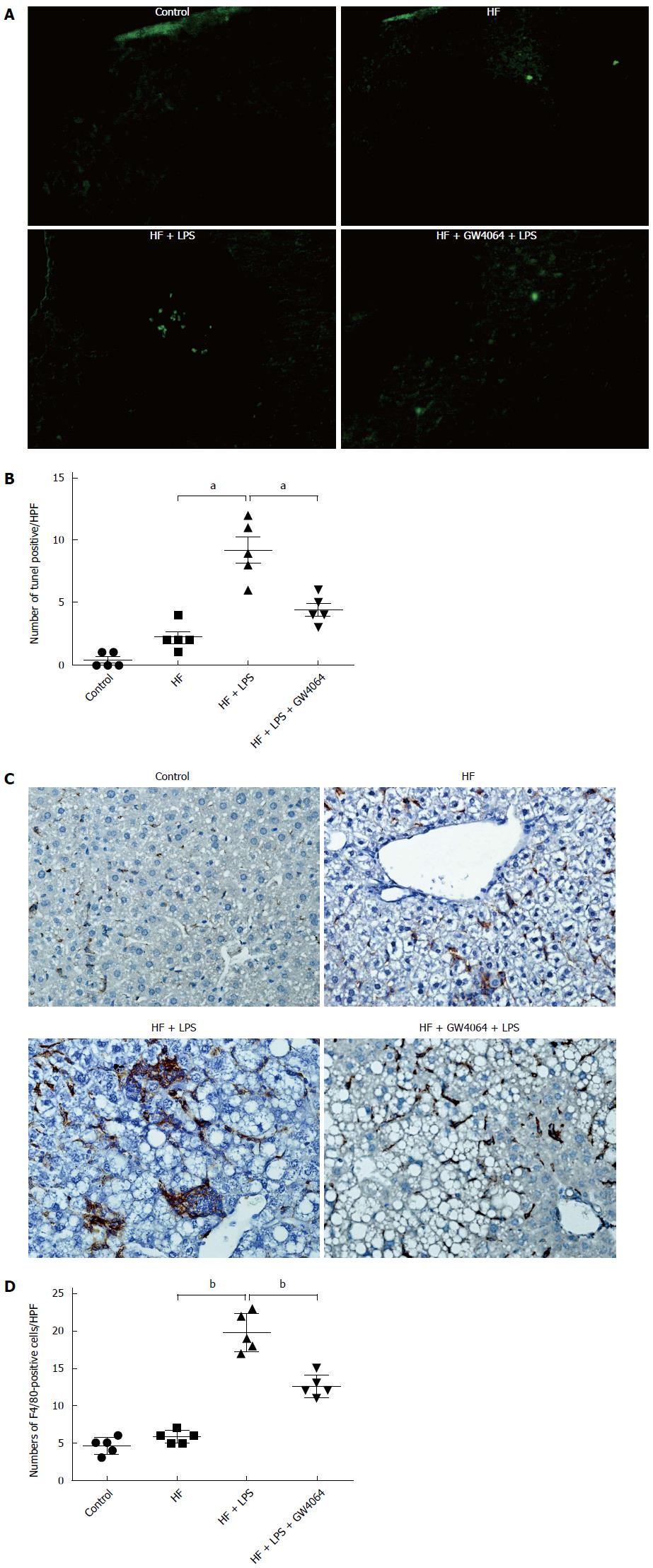
Figure 2 GW4064 reduces apoptosis and macrophage infiltration in a murine nonalcoholic fatty liver disease model.
A: Representative terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining of liver sections (magnification × 400) from normal diet, high-fat (HF), HF + lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and HF + GW4064 + LPS mice; B: Quantification of TUNEL in each high power field (HPF); C: Representative immunohistochemical staining of F4/80 in the livers (magnification × 400) of normal diet, HF, HF + LPS, and HF + GW4064 + LPS mice; D: Quantification of F4/80-positive cells in each HPF. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs HF + LPS group.
- Citation: Yao J, Zhou CS, Ma X, Fu BQ, Tao LS, Chen M, Xu YP. FXR agonist GW4064 alleviates endotoxin-induced hepatic inflammation by repressing macrophage activation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(39): 14430-14441
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i39/14430.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14430