Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2014; 20(39): 14420-14429
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14420
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14420
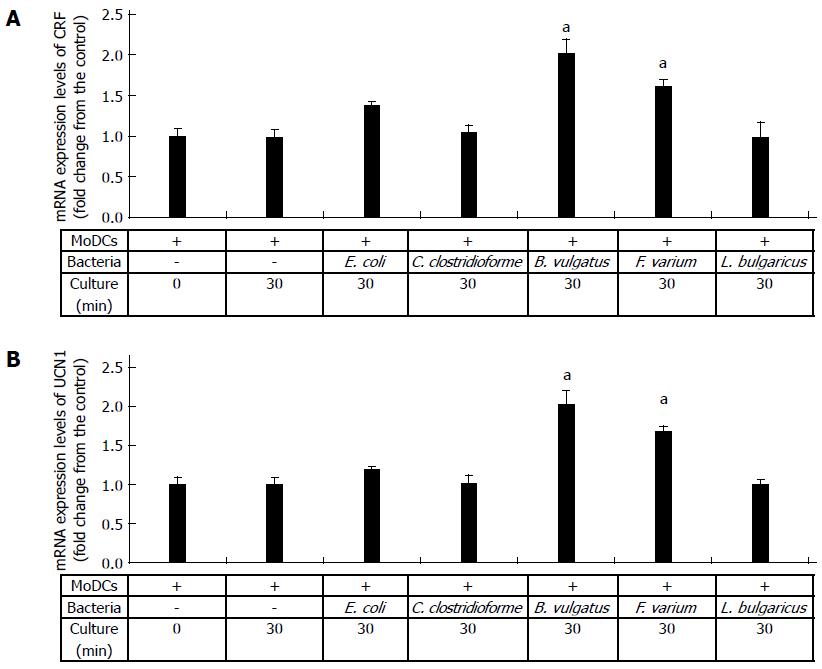
Figure 2 Detection of corticotropin-releasing factor and urocortin 1 mRNA in dendritic cells stimulated with commensal bacteria.
Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs) were stimulated with Escherichia coli (E. coli), Clostridium clostridioforme (C. clostridioforme), Bacteroides vulgatus (B. vulgatus), Fusobacterium varium (F. varium), and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus (L. bulgaricus) for 30 min, and A: corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and B: urocortin 1 (UCN1) mRNA were analyzed. Human MoDCs were cultured alone for 0 and 30 min and used as controls. CT values reflect the polymerase chain reaction cycle number at which the amount of amplified target reached a fixed threshold. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD from 3 repeated experiments. aP < 0.05 vs other groups.
- Citation: Koido S, Ohkusa T, Kan S, Takakura K, Saito K, Komita H, Ito Z, Kobayashi H, Takami S, Uchiyama K, Arakawa H, Ito M, Okamoto M, Kajihara M, Homma S, Tajiri H. Production of corticotropin-releasing factor and urocortin from human monocyte-derived dendritic cells is stimulated by commensal bacteria in intestine. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(39): 14420-14429
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i39/14420.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14420