Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2014; 20(39): 14420-14429
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14420
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14420
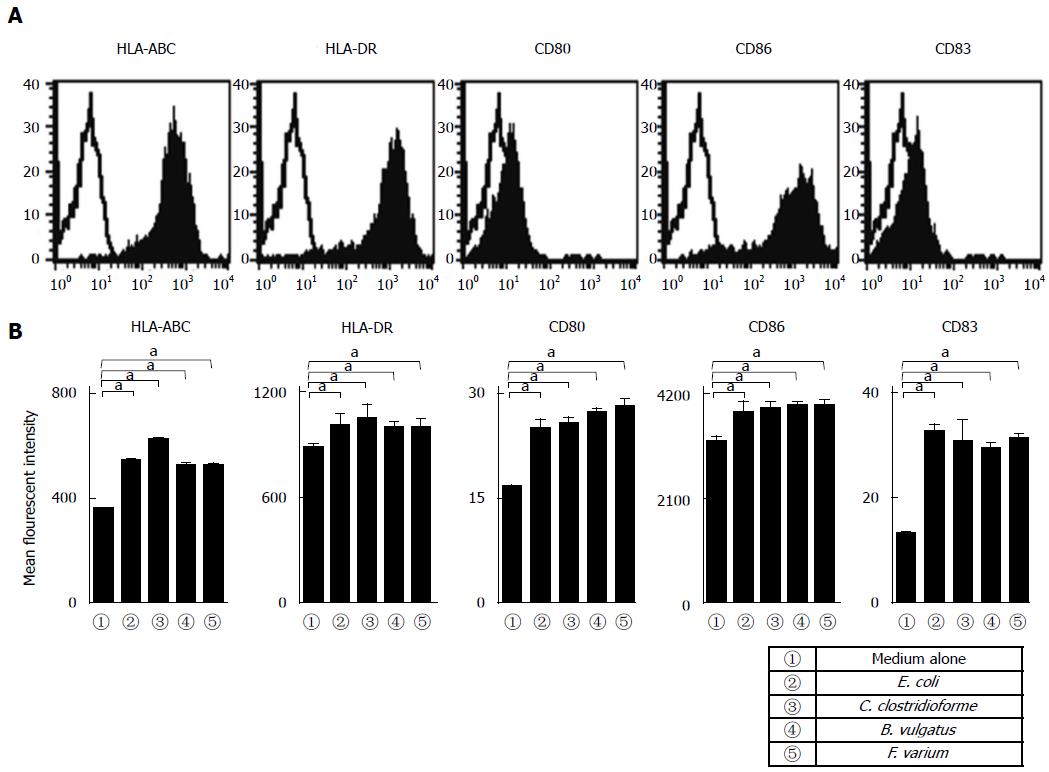
Figure 1 Phenotypic characterization of dendritic cells.
A: Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs) were analyzed using flow cytometry for expression of the indicated antigens (n = 5). Unfilled histogram profiles indicate the isotype control, and solid histograms indicate the specific antibodies; B: Analysis of the mean fluorescence intensity of the indicated molecules expressed in MoDCs stimulated with commensal bacteria (n = 5). Unstimulated MoDCs were used as a control. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Koido S, Ohkusa T, Kan S, Takakura K, Saito K, Komita H, Ito Z, Kobayashi H, Takami S, Uchiyama K, Arakawa H, Ito M, Okamoto M, Kajihara M, Homma S, Tajiri H. Production of corticotropin-releasing factor and urocortin from human monocyte-derived dendritic cells is stimulated by commensal bacteria in intestine. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(39): 14420-14429
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i39/14420.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14420