Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2014; 20(37): 13530-13537
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13530
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13530
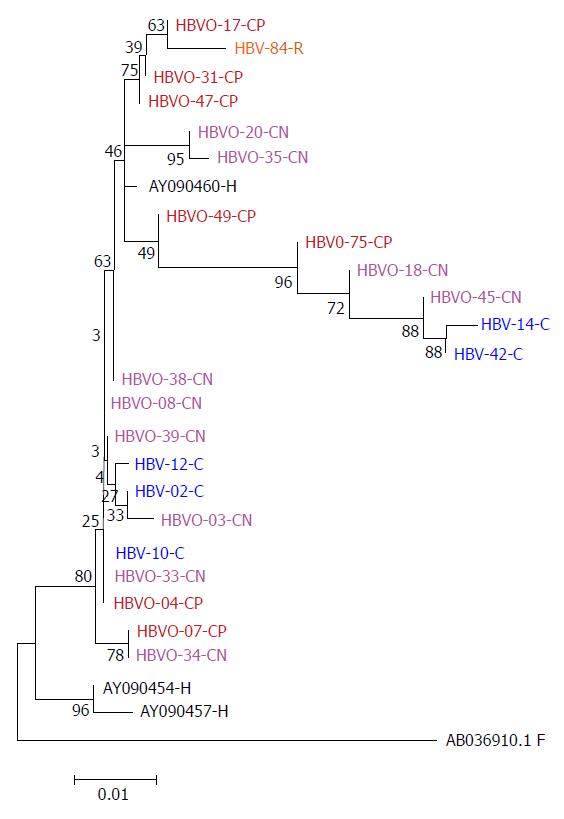
Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree constructed by the Maximum Likelihood method based on the partial nucleotide sequence of the core gen (439 bp) of 18 OHBI isolates (CP and CN); 5 sequences (C) obtained from hepatitis B virus overt co-infection (HbsAg+), using the three genotype H reference sequences from Genbank (AB375159.
1, AB375160.1, AB375161.1), as a reference group and one hepatitis B virus sequence from a chronic hepatitis B virus mono-infected patient (HBV-84-R). Genetic distances were estimated using the Kimura two-parameter matrix and Bootstrap values are indicated for the major nodes as a percentage of the data obtained from 1000 replicates. C: Core; -CN: Seronegative OHBI; -CP: Seropositive OHBI; -S: HBsAg+ isolates.
- Citation: Alvarez-Muñoz MT, Maldonado-Rodriguez A, Rojas-Montes O, Torres-Ibarra R, Gutierrez-Escolano F, Vazquez-Rosales G, Gomez A, Muñoz O, Torres J, Lira R. Occult hepatitis B virus infection among Mexican human immunodeficiency virus-1-infected patients. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(37): 13530-13537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i37/13530.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13530