Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2014; 20(37): 13521-13529
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13521
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13521
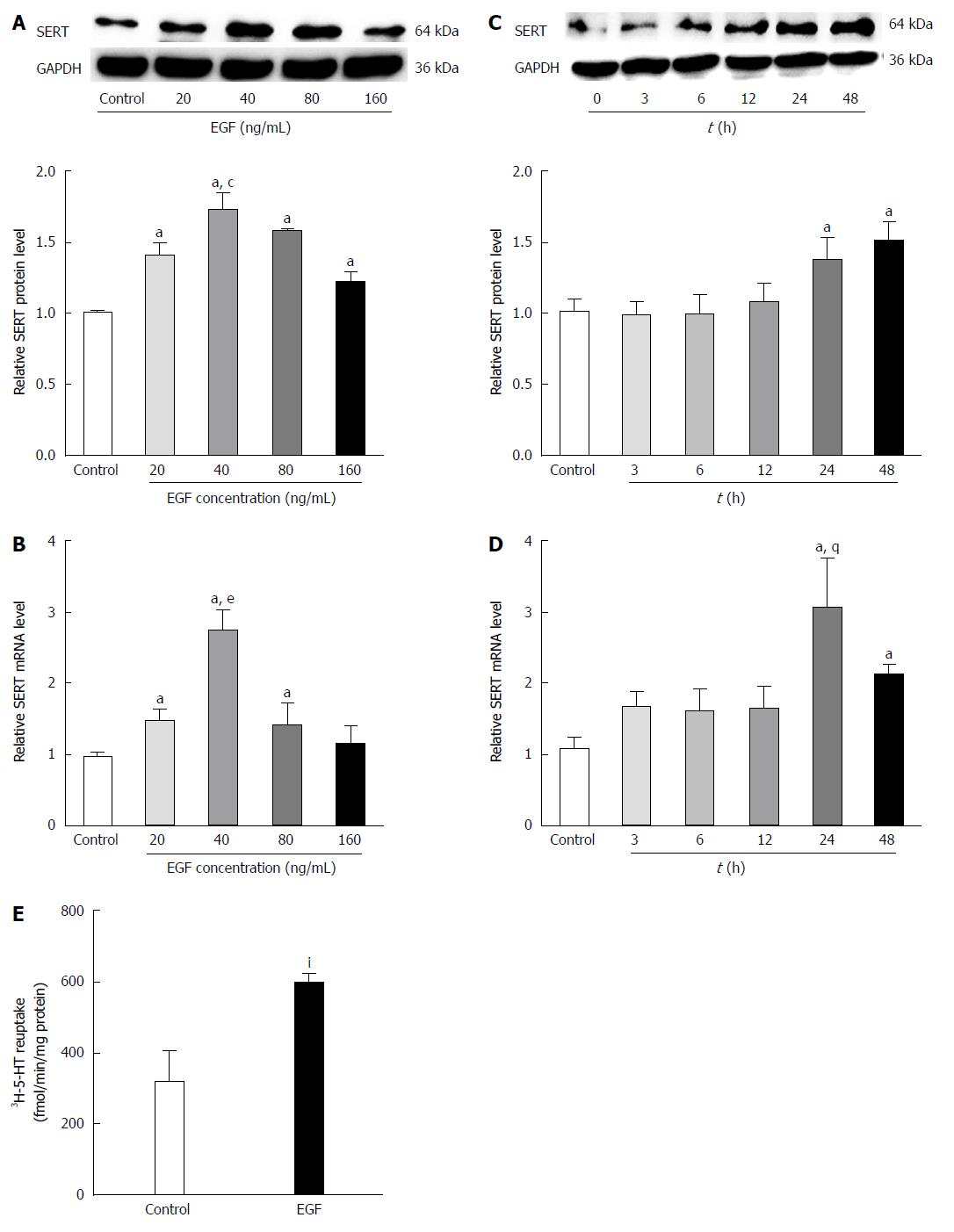
Figure 4 Effects of epidermal growth factor on serotonin transporter in rat intestinal epithelial cells.
Intestinal epithelial cells (IEC-6) cells were treated with epidermal growth factor (EGF) (0, 20, 40, 60, and 80 ng/mL) for 24 h. A: Western blots were performed to detected serotonin transporter (SERT) protein expressions. GAPDH was used to verify equivalent protein loading (aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs 20, 80, and 160 ng/mL); B: SERT gene expression was examined by real-time PCR (aP < 0.05 vs control; eP < 0.05 vs 20 and 80 ng/L). To determine the optimal time for EGF treatment, IEC-6 cells were treated with EGF (40 ng/L) for the indicated times (0, 3, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h); C: SERT protein levels were examined by Western blot (aP < 0.05 vs control); D: SERT gene expression was examined by real-time PCR (aP < 0.05 vs control; gP < 0.05 vs 48 h); E: Uptake of [3H]-serotonin in cells pre-treated with 40 ng/ml EGF for 24 h (IP < 0.05 vs 24 h) . All values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
- Citation: Cui XF, Zhou WM, Yang Y, Zhou J, Li XL, Lin L, Zhang HJ. Epidermal growth factor upregulates serotonin transporter and its association with visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(37): 13521-13529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i37/13521.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13521