Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2014; 20(37): 13521-13529
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13521
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13521
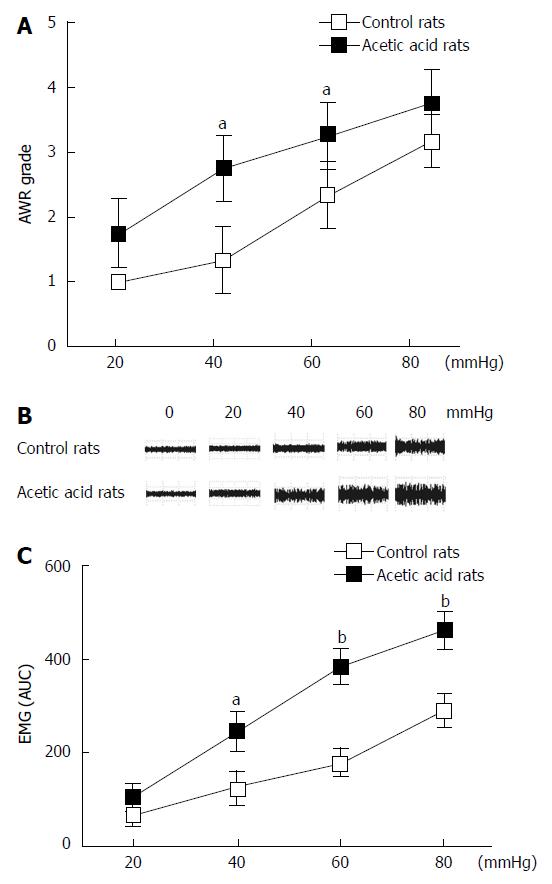
Figure 1 Effect of neonatal acetic acid treatment on 8-wk-old rat sensitivity to colorectal distension.
A: Abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) responses to the graded pressures of colorectal distension (CRD) in saline-treated (n = 10) and acetic acid-treated (n = 10) rats. Acetic acid-treated rats show increased AWR scores compared with the saline rats. Values are expressed as mean ± SD; B: Representative electromyogram (EMG) traces recorded in control and acetic acid-treated rats in response to CRD; C: EMG responses to CRD in rats treated with saline and acetic acid at the neonatal stage. Similar to the AWR scores, acetic acid-treated rats exhibited exaggerated EMG activity responses to CRD at different pressures compared with the saline-treated rats. Neonatal rats vs control rats, aP < 0.05, bP≤ 0.01, error bars represent the mean ± SD.
- Citation: Cui XF, Zhou WM, Yang Y, Zhou J, Li XL, Lin L, Zhang HJ. Epidermal growth factor upregulates serotonin transporter and its association with visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(37): 13521-13529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i37/13521.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13521