Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2014; 20(37): 13466-13476
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13466
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13466
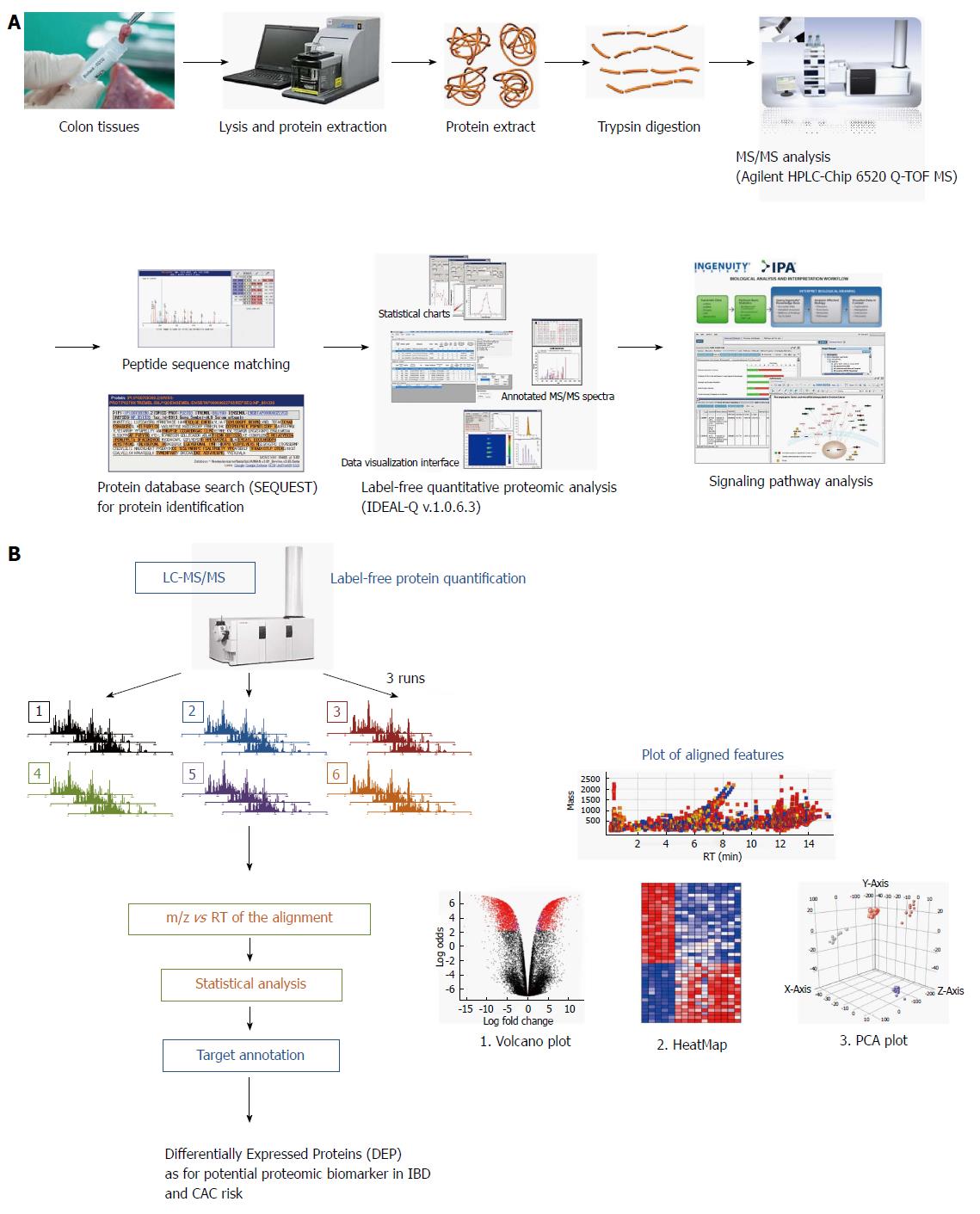
Figure 1 Schematic presentation showing proteome analysis to discover potential biomarkers and label-free quantification analysis in inflammatory bowel disease.
A: Applying the label-free quantification method to discover proteomic biomarkers in patients with different types and different stage of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Comparative analysis was done in eight patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), eight patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and eight patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Biopsied colon tissues were obtained during colonoscopy after written consent, and stored in a deep freeze until assayed. Using Agilent HPLC-Chip 6520 Q-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF-MS) and label-free quantitative proteome analysis (IDEAL-Q v1.0.6.3), significant signal pathway analysis was done. In the current review, the analysis done according to the degree of intestinal inflammation, type of IBD, and extent of inflammation from 24 patients, eight from non-IBD normal patients; i.e., IBS patients, eight from patients with UC, and from patients with CD; B: Label-free protein quantification scheme for potential biomarker for colitis-associated cancer (CAC) risk in 16 patients with IBD.
- Citation: Park JM, Han NY, Han YM, Chung MK, Lee HK, Ko KH, Kim EH, Hahm KB. Predictive proteomic biomarkers for inflammatory bowel disease-associated cancer: Where are we now in the era of the next generation proteomics? World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(37): 13466-13476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i37/13466.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13466