Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2014; 20(36): 13105-13118
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13105
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13105
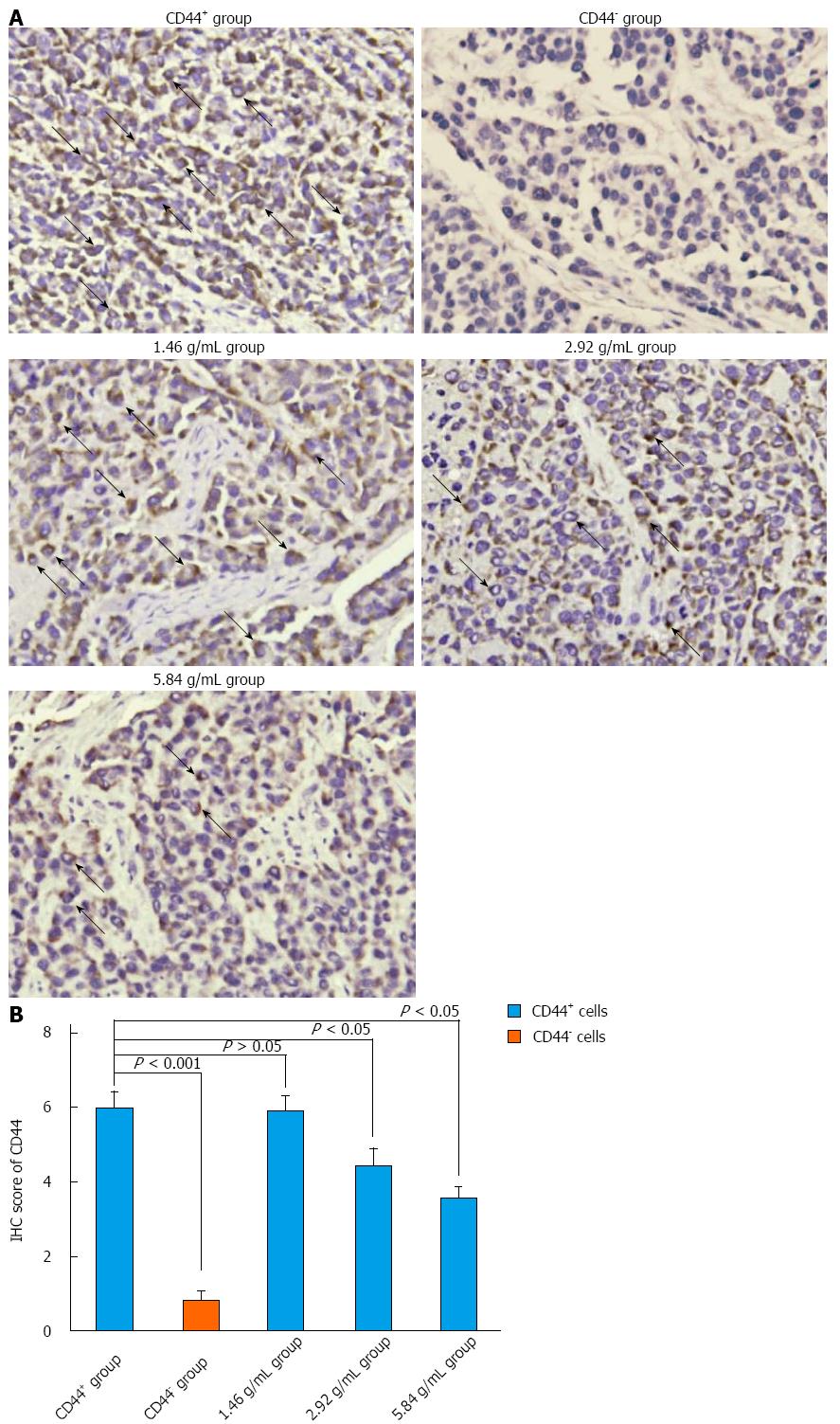
Figure 5 Xiaotan Sanjie decoction inhibits CD44 expression in a dose-dependent manner.
A: Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for CD44. CD44 was highly expressed in the cancer cell membrane (original magnification × 400, positive areas are indicated by black arrows); B: The comparison of CD44 in different groups. CD44 was highly expressed in the control CD44+ group compared with the rest of the groups and was rarely detected in the control CD44- group. The results also showed that not all of the cells in the CD44+ group were CD44 positive. Xiaotan Sanjie decoction inhibited the expression of CD44 in a dose-dependent manner. Statistically significant differences in the expression of CD44 were also detected in the medium- and high-dose groups in CD44+ cells (nonparametric tests).
- Citation: Yan B, Liu L, Zhao Y, Xiu LJ, Sun DZ, Liu X, Lu Y, Shi J, Zhang YC, Li YJ, Wang XW, Zhou YQ, Feng SH, Lv C, Wei PK, Qin ZF. Xiaotan Sanjie decoction attenuates tumor angiogenesis by manipulating Notch-1-regulated proliferation of gastric cancer stem-like cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(36): 13105-13118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i36/13105.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13105