Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2014; 20(36): 13088-13104
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13088
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13088
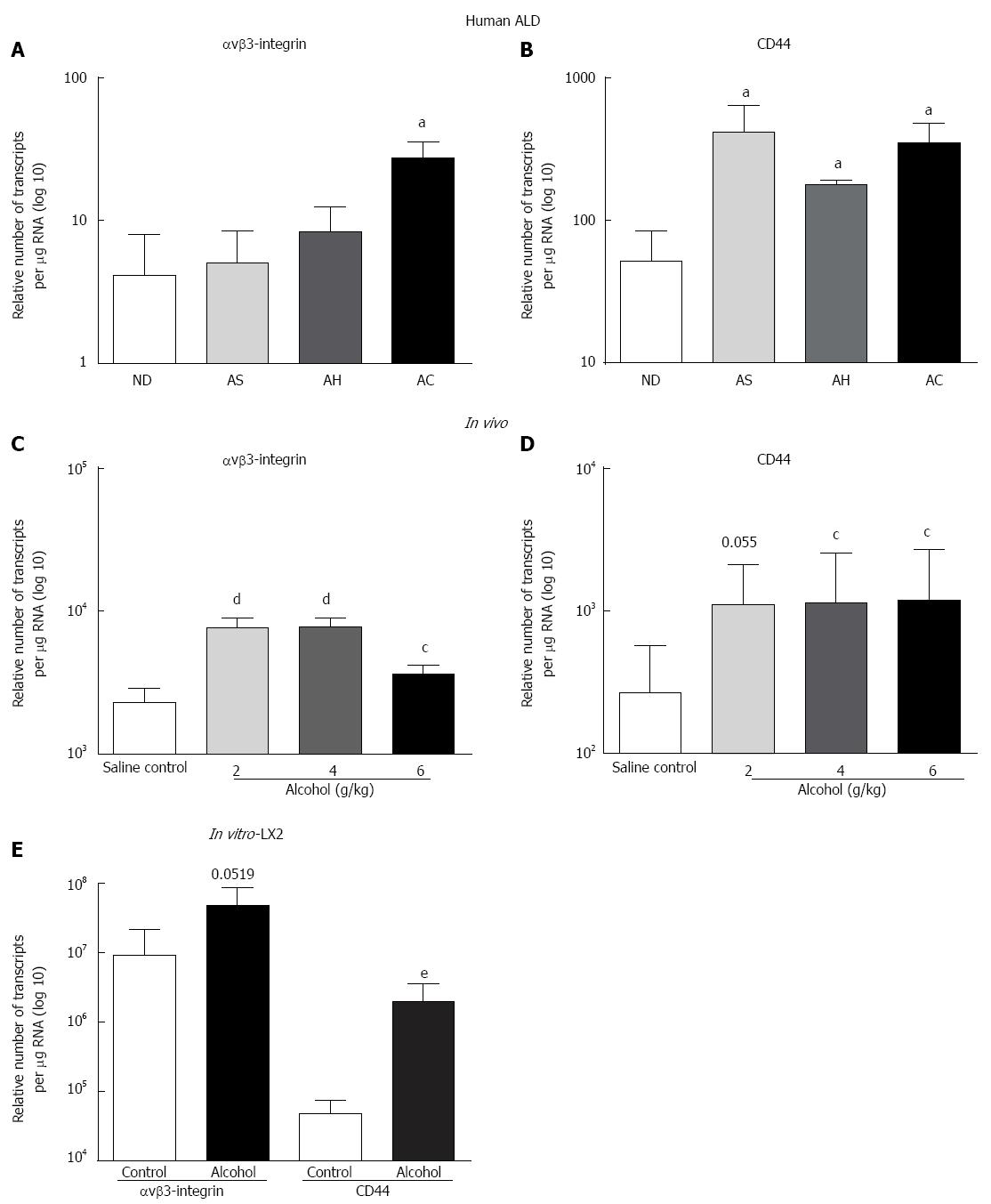
Figure 2 Increased expression of over-expression of Osteopontin cognate receptors αvβ3-integrin and CD44 in human alcoholic liver disease; in vivo in mice and in vitro in LX2 cells with a single acute dose of alcohol.
Increase in αvβ3-integrin mRNA (transcripts per ìg total RNA) was observed with disease progression in human alcoholic liver disease (ALD), but only reached significance in alcoholic cirrhosis (AC) compared to non-diseased (ND) (A); CD44v6 mRNA significantly increased in all ALD stages (B). In vivo, all alcohol doses significantly increased mRNA expression of αvβ3-integrin (C) but CD44 reached significance only at 4 g/kg and 6 g/kg (D). Alcohol (10 mmo/L per 4 h) also increased both αvβ3-integrin and CD44 mRNA expression in LX2 cells compared to control (E). aP < 0.05 vs ND; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs saline control; eP < 0.01 vs control. AS: Alcoholic steatosis; AH: Alcoholic hepatitis.
-
Citation: Seth D, Duly A, Kuo PC, McCaughan GW, Haber PS. Osteopontin is an important mediator of alcoholic liver disease
via hepatic stellate cell activation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(36): 13088-13104 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i36/13088.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.13088