Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2014; 20(36): 12767-12780
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12767
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12767
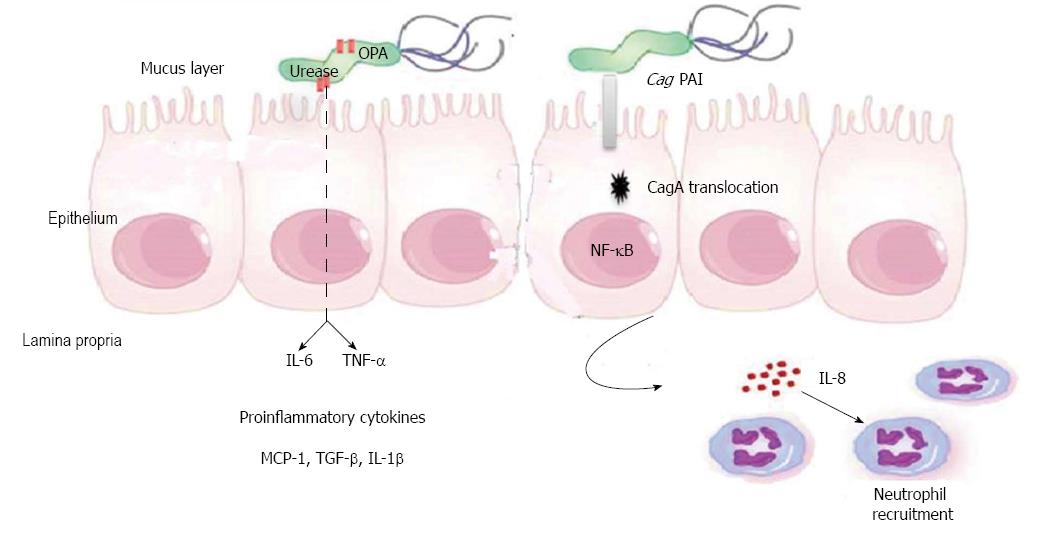
Figure 3 Cytokines production by gastric epithelial cell during Helicobacter pylori Infection.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) leads to production of proinflammatory cytokines by gastric epithelial cells (GECs). Interactions between the translocated cagA and gastric epithelial cells lead to activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB, alteration in gene transcription in the GECs, and secretion of IL-8 by GECs, which leads to recruitment of neutrophils. H. pylori urease induces the production of IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) by GECs. Other cytokines secreted by GECs during H. pylori infection such as, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-1α, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), migration inhibitory factor and tumor growth factor (TGF)-α.
-
Citation: Alzahrani S, Lina TT, Gonzalez J, Pinchuk IV, Beswick EJ, Reyes VE. Effect of
Helicobacter pylori on gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(36): 12767-12780 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i36/12767.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12767