Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2014; 20(36): 12713-12721
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12713
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12713
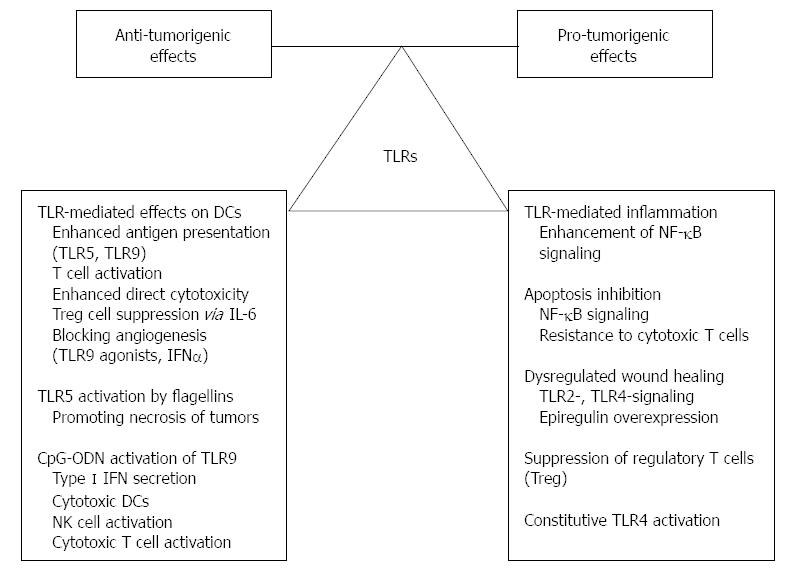
Figure 2 Dual role of Toll-like receptor signaling in colitis-associated carcinogenesis.
While some direct and indirect effects of TLR-signaling act largely as an anti-tumorigenic factors, other effects may promote cancer development. TLR: Toll-like receptor; DC: Dendritic cell; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon; ODN: Oligodeoxynucleotide; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
- Citation: Sipos F, Fűri I, Constantinovits M, Tulassay Z, Műzes G. Contribution of TLR signaling to the pathogenesis of colitis-associated cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(36): 12713-12721
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i36/12713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12713