Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2014; 20(35): 12551-12558
Published online Sep 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12551
Published online Sep 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12551
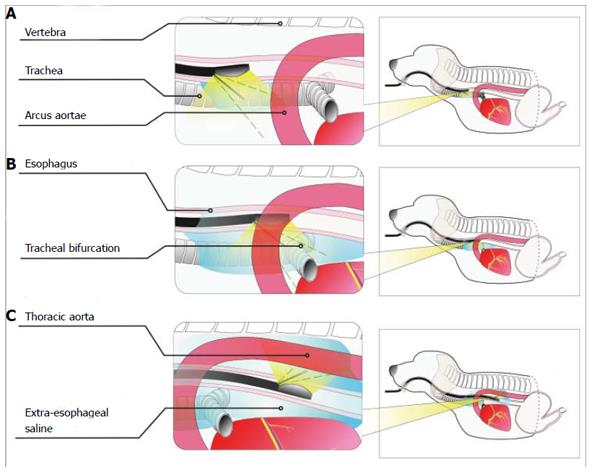
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of extraesophageal puncture in different sections.
A: Positioning of the puncture point in the upper thoracic segment. The puncture point was located in the anterior esophageal wall to distinguish between the trachea and the esophagus and between the left upper large thoracic vessels and the esophagus; B: Positioning of the puncture point in the middle thoracic segment. The puncture point was located in the anterior esophageal wall to distinguish between the bronchial bifurcation and the esophagus and between the arcus aortae and the esophagus; C: Positioning of the puncture point in the lower thoracic segment. The puncture point was located in the posterior esophageal wall to distinguish between the thoracic aorta and the esophagus.
- Citation: Li JJ, Shan HB, He LJ, Wang TD, Xiong H, Chen LM, Li XH, Huang XX, Luo GY, Li Y, Xu GL. Extraesophageal saline enhances endoscopic ultrasonography to differentiate esophagus and adjacent organs. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(35): 12551-12558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i35/12551.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12551