Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2014; 20(34): 12161-12170
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12161
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12161
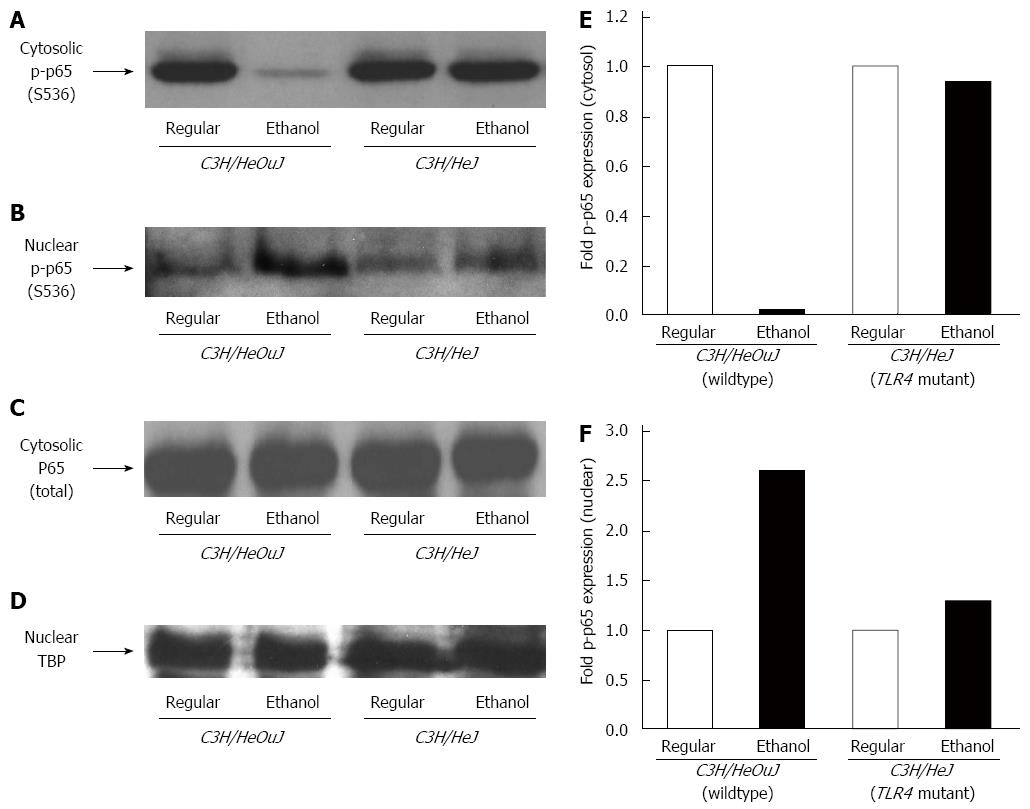
Figure 3 Nuclear factor-κB phosphorylation.
Cytosolic (A, C) and nuclear (B, D) protein fractions isolated from the livers of C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice pair-fed with regular and ethanol-containing diets were used for western blots to detect phosphorylated (serine 536) p65 (p-p65) expression. Anti-total p65 (p65) (C) and anti-TATA-binding protein (TBP) (D) antibodies were used as controls. Cytosolic (E) and nuclear (F) p-p65 expression was quantified by densitometric analysis and normalized to total p65 or TBP protein expression, respectively. Normalized p-p65 expression in ethanol-fed mice was expressed as fold expression of that in the respective mice pair-fed with the regular diet (mean; n = 3 per group).
- Citation: Zmijewski E, Lu S, Harrison-Findik DD. TLR4 signaling and the inhibition of liver hepcidin expression by alcohol. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(34): 12161-12170
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i34/12161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12161