Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2014; 20(33): 11894-11903
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11894
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11894
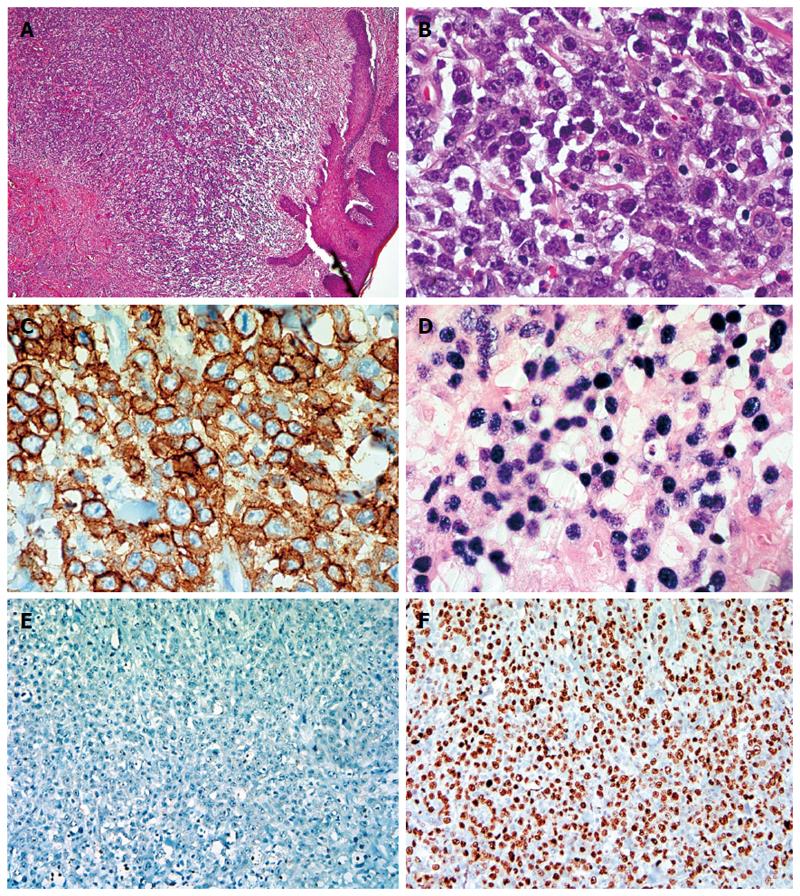
Figure 1 Microscopic examination.
A: Microscopic examination of rectal biopsy showed intact squamous mucosa with submucosal dense lymphoid infiltrate associated with increased angiogenesis (HE, magnification × 40); B: High power view demonstrated sheets of large a typical lymphoid cells with plasmablastic differentiation (big round to oval nuclei, dense or disperse chromatin, prominent nucleoli and abundant amphophilic cytoplasm with increased apoptosis and mitosis and scattered inflammatory cells (HE, magnification × 600); C: CD138 immunostain highlighting the neoplastic cells (Immunoperoxidase, magnification × 600); D: In situ hybridization by using epstein barr virus -encoded RNA probe showed diffuse and strong signals (ISH, magnification × 600); E: Plasmablastic lymphoma cells being purely negative for CD20 (Immunoperoxidase, magnification × 100); F: High proliferation index was highlighted by Ki67 immunostain (approximately 80%) (Immunoperoxidase, Magnification × 100).
- Citation: Luria L, Nguyen J, Zhou J, Jaglal M, Sokol L, Messina JL, Coppola D, Zhang L. Manifestations of gastrointestinal plasmablastic lymphoma: A case series with literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(33): 11894-11903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i33/11894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11894