Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2014; 20(33): 11865-11870
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11865
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11865
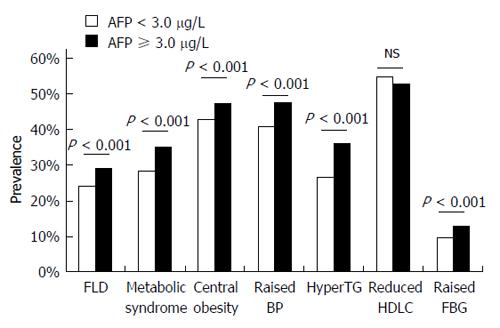
Figure 1 Prevalence of fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome, and its components in subjects with different serum alpha-fetoprotein levels.
Subjects were classified into two groups according to the median level of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) (3.0 μg/L). Significantly higher prevalence of fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome, and its components including central obesity, elevated blood pressure (BP), hypertriglyceridemia (hyperTG), and elevated fasting blood glucose (FBG) were observed in subjects with serum AFP ≥ 3.0 μg/L compared with those with serum AFP < 3.0 μg/L. FLD: Fatty liver disease; HDLC: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; FBG: Fasting blood glucose.
- Citation: Xu P, Xu CF, Wan XY, Yu CH, Shen C, Chen P, Xu GY, Li YM. Association between serum alpha-fetoprotein levels and fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(33): 11865-11870
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i33/11865.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11865