Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2014; 20(33): 11856-11864
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11856
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11856
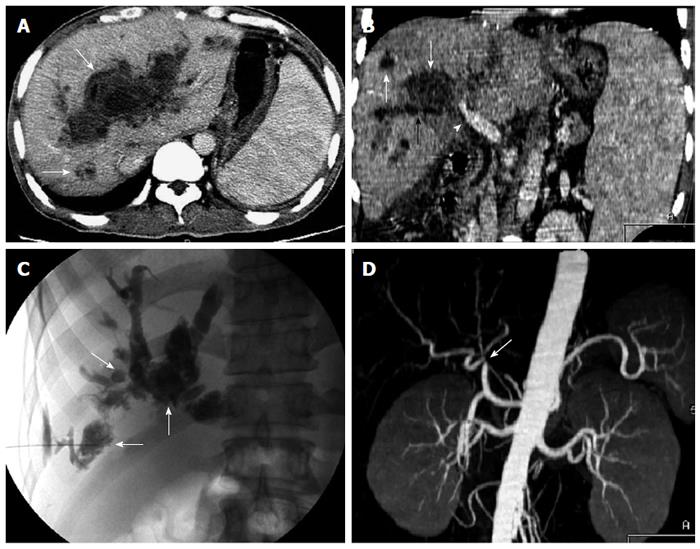
Figure 5 A 46-year-old man with jaundice and fever due to biloma or biligenic hepatic abscess 4 mo after orthotopic liver transplantation.
Transverse computed tomography (CT) image in the portal venous phase (A) and oblique reformat image (B) show multiple biloma or biligenic hepatic abscess (white arrow) communicating with the dilated bile ducts (black arrow), and stenosis of the hepatic hilar bile duct (arrowhead); C: Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography demonstrates biliary dilation, necrosis, and abscess cavity (contrast medium pool) (arrow); D: CT angiography shows hepatic arterial anastomotic stenosis (arrow).
- Citation: Meng XC, Huang WS, Xie PY, Chen XZ, Cai MY, Shan H, Zhu KS. Role of multi-detector computed tomography for biliary complications after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(33): 11856-11864
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i33/11856.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11856