Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2014; 20(33): 11856-11864
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11856
Published online Sep 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11856
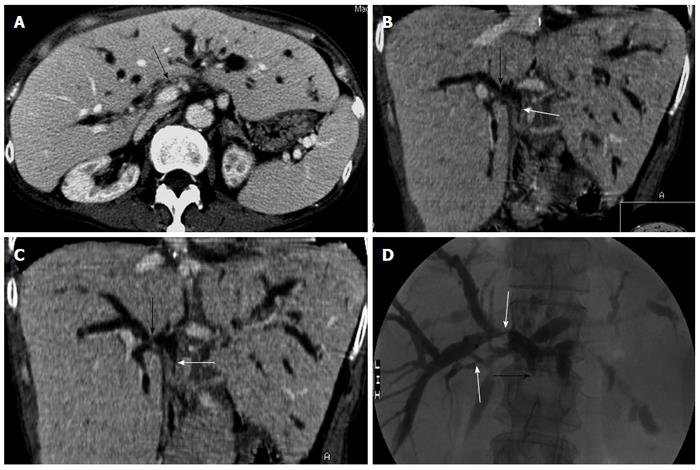
Figure 2 A 66-year-old women with obstructive jaundice due to nonanastomotic biliary strictures 11 mo after orthotopic liver transplantation.
A: Transverse computed tomography (CT) image on the portal venous phase shows marked stenosis of the hepatic hilar bile duct (arrow) and dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts; B,C: CT oblique reformat image shows biliary stenosis at the hepatic bifurcation (black arrow) and the donor common duct (white arrow); D: Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography demonstrates the stenosis of intrahepatic bile duct and hepatic bifurcation (white arrow), and complete occlusion of the donor common duct (black arrow).
- Citation: Meng XC, Huang WS, Xie PY, Chen XZ, Cai MY, Shan H, Zhu KS. Role of multi-detector computed tomography for biliary complications after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(33): 11856-11864
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i33/11856.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11856