Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2014; 20(32): 11297-11304
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11297
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11297
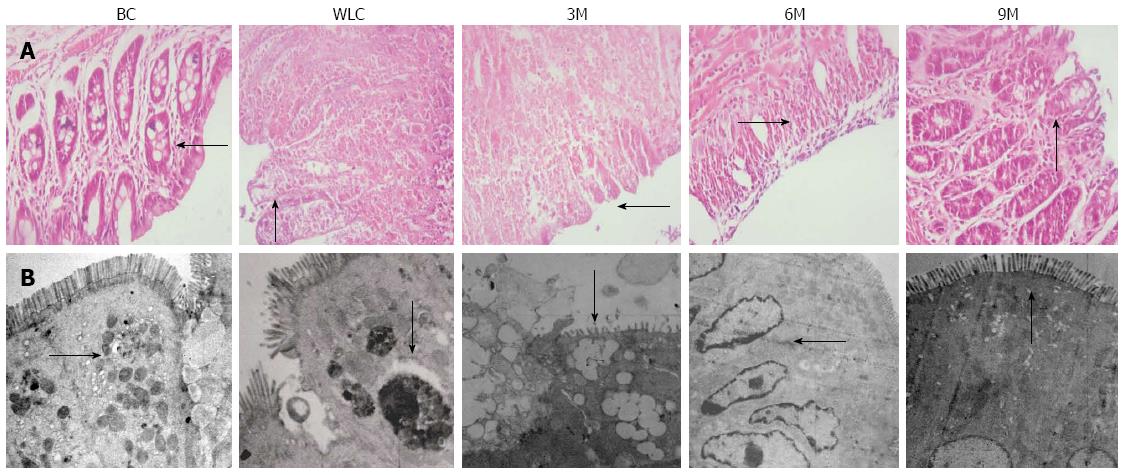
Figure 3 Histological features and morphology of colonic tissue.
A: Histological analysis of colonic tissue sections stained with HE. The finer details of the epithelial cells can be seen clearly; B: Morphology of colonic mucosal epithelia observed by electron microscopy. From left to right in both A and B: Blank control (BC), waiting list control (WLC), 3-min moxibustion (3M), 6-min moxibustion (6M) and 9-min moxibustion (9M) groups. Treatment in the 9M group gave the best results, which were close to that of the normal rats without ulcerative colitis. Black arrow: Representative features of colonic tissue (magnification: A: 400 ×; B: 2000 ×).
- Citation: Han Y, Ma TM, Lu ML, Ren L, Ma XD, Bai ZH. Role of moxibustion in inflammatory responses during treatment of rat ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(32): 11297-11304
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i32/11297.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11297