Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2014; 20(32): 11033-11053
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11033
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11033
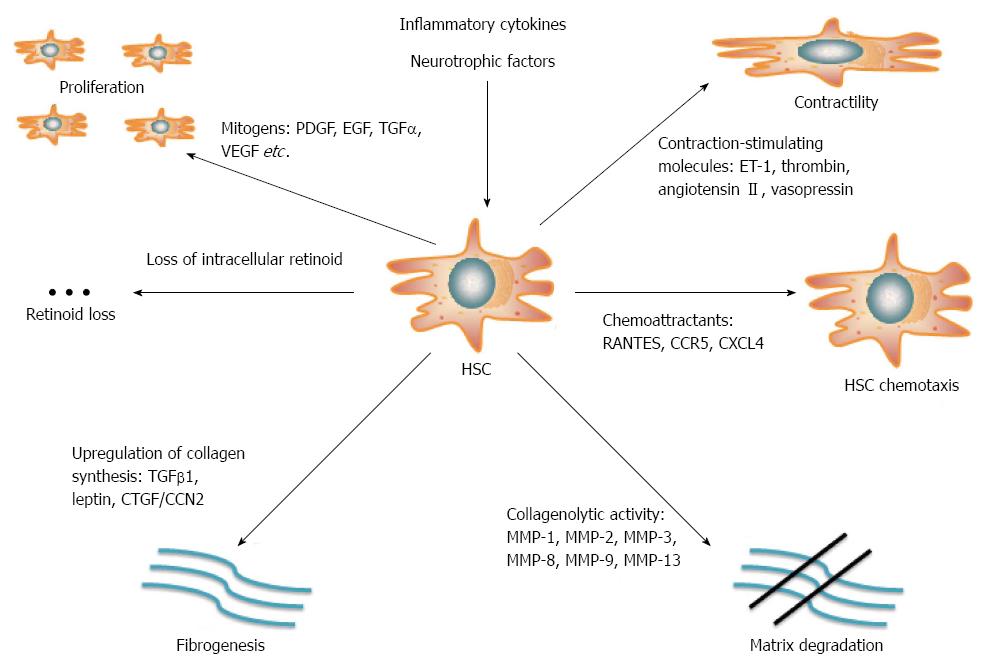
Figure 1 Hepatic stellate cells are retinoid-storing cells that play a key role in liver fibrogenesis.
During liver injury, they undergo transformation from a quiescent state to proliferative, contractile myofibroblasts. Activated HSCs are the main source for production of collagen and other ECM proteins. Several molecules and pathways regulate the equilibrium between deposition and degradation of ECM proteins. HSCs: Hepatic stellate cells; ECM: Extracellular matrix; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; CCR5: C-C chemokine receptor 5; MMP-2: Matrix metalloproteinase 2.
- Citation: Sebastiani G, Gkouvatsos K, Pantopoulos K. Chronic hepatitis C and liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(32): 11033-11053
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i32/11033.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11033