Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2014; 20(31): 10908-10915
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10908
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10908
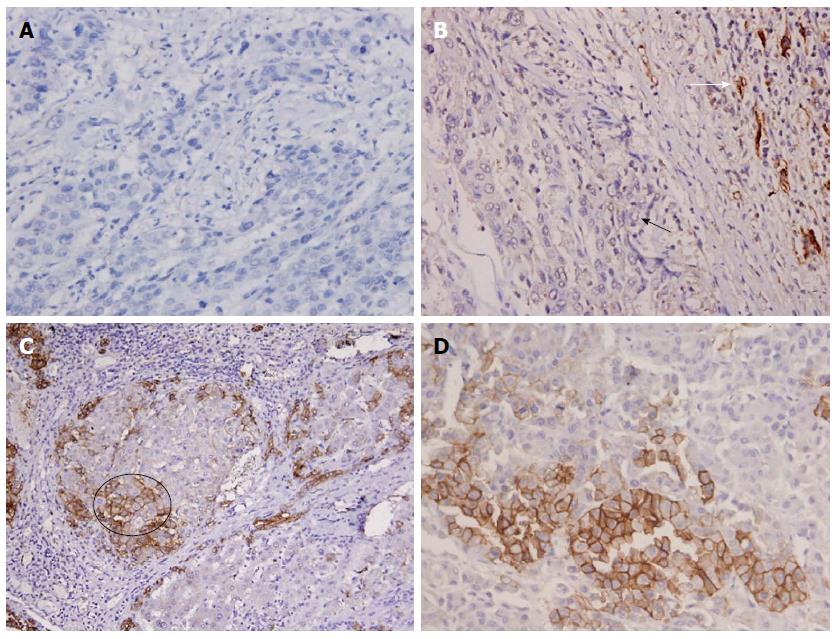
Figure 1 Immunohistochemistry staining pictures.
Diffuse loss of DR/EpCAM in HCC > 3 cm (A, IHC, × 400), a surgical sample of HCC ≤ 3 cm (a moderately differentiated HCC), and the area of foci invasion (black arrow) in HCC ≤ 3 cm; the invasive area showed diffuse loss of DR/EpCAM; but positive on the biliary cells between hepatic lobules (white arrow) (B, IHC, × 400). Active DR/EpCAM was observed in a cirrhotic nodule (C, IHC, × 200), and part of liver cells were EpCAM positive (circle). DR/EpCAM was focally positive (D, IHC, × 400), and the cells showed features of hepatocyte inside the nodules of HCCs. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; DR: Ductular reaction; EpCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; IHC: Immunohistochemistry.
- Citation: Zhang Q, Zhang CS, Xin Q, Ma Z, Liu GQ, Liu BB, Wang FM, Gao YT, Du Z. Perinodular ductular reaction/epithelial cell adhesion molecule loss in small hepatic nodules. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(31): 10908-10915
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i31/10908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10908