Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2014; 20(31): 10876-10885
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10876
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10876
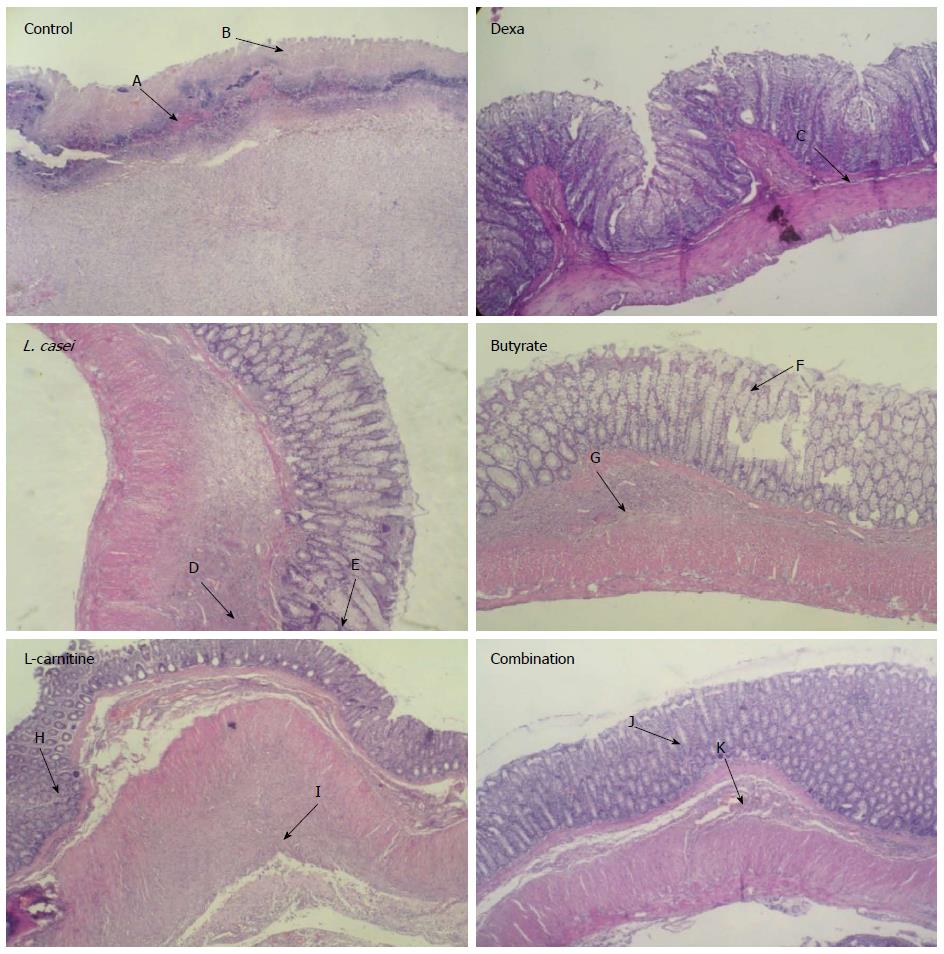
Figure 1 Histological images of colon tissues from control and experimental groups.
Microscopic evaluation of Control group showed transmural inflammation and/or diffuse necrosis hemorrhage (A) and severe crypt destruction (B). In histological examination of Dexa group, minimal mucosal inflammation was observed (C). In L. casei and Butyrate groups, mild infiltration (D, G) and crypt destruction (E, F) were seen. In L-carnitine group, crypt formation (H), submucosa inflammation and low PMN infiltration (I) were observed. In Combination group, crypt abscess (J) and normal submucosa (K) were evident.
-
Citation: Moeinian M, Ghasemi-Niri SF, Mozaffari S, Abdolghaffari AH, Baeeri M, Navaea-Nigjeh M, Abdollahi M. Beneficial effect of butyrate,
Lactobacillus casei and L-carnitine combination in preference to each in experimental colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(31): 10876-10885 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i31/10876.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10876