Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2014; 20(31): 10813-10824
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10813
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10813
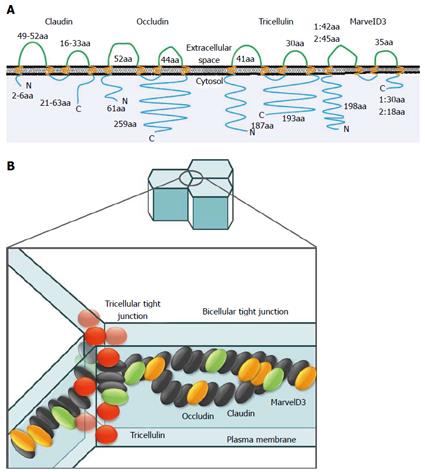
Figure 1 Claudins, occludin, tricellulin, marvelD3 and junctional adhesion molecules.
A: Schematic representation of human claudin, occludin, tricellulin, and marvelD3. These molecules contain four transmembrane domains with two extracellular loops. Claudins consist of at least 27 members. Occludin has several variants. MarvelD3 has two isoforms. aa: amino acid; B: Models of tight junction protein locations in paracellular space. The bicellular tight junction is the interface between two cells, whereas the vertex where three cells meet is termed the tricellular tight junction. The tight junction strands within both bicellular and tricellular regions are composed of claudins (black ellipses). MarvelD3 (green ellipses), occludin (orange ellipses), and tricellulin (red spheres) incorporated into claudin-based tight junction strands. Occludin and tricellulin are primarily found at bicellular and tricellular regions, respectively, whereas marvelD3 is present at both sites. Tricellulin is unique in that it is present at the tight junction and along the lateral membrane.
- Citation: Kyuno D, Yamaguchi H, Ito T, Kono T, Kimura Y, Imamura M, Konno T, Hirata K, Sawada N, Kojima T. Targeting tight junctions during epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(31): 10813-10824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i31/10813.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10813