Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2014; 20(30): 10553-10563
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10553
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10553
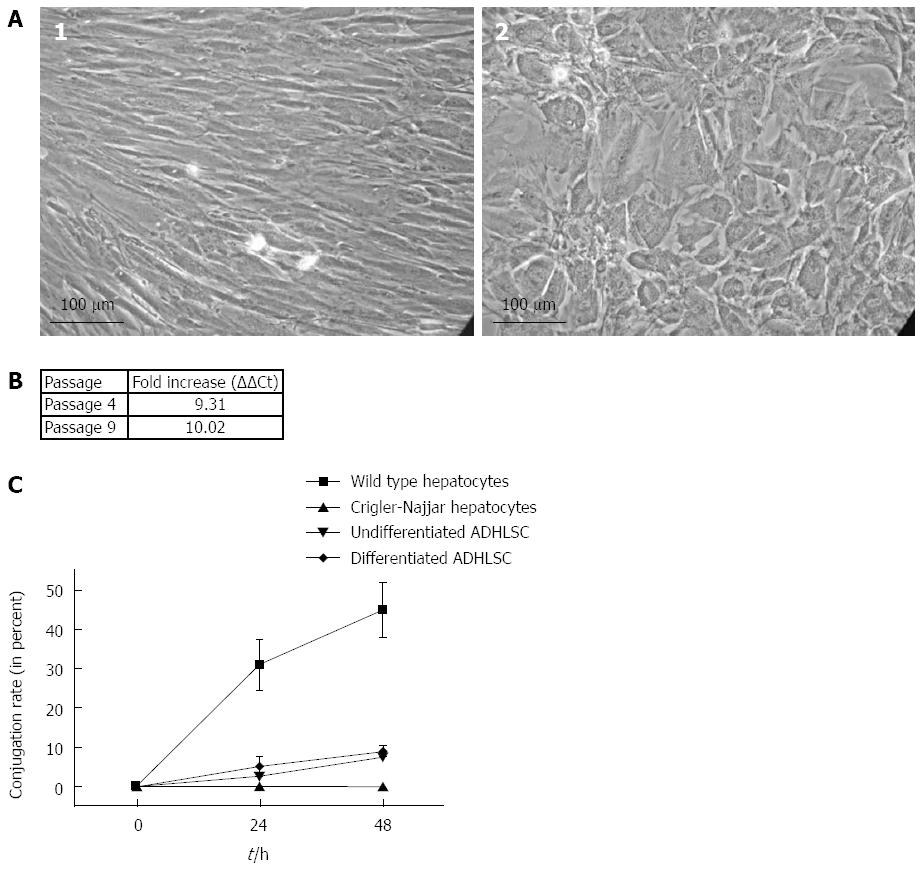
Figure 2 Hepatogenic differentiation and expression of functional uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1.
A: Evaluation of in vitro adult-derived human liver stem/progenitor cells (ADHLSC) hepatic differentiation potential at passage 6. Undifferentiated ADHLSC (1) were able to change their morphology by adopting a polygonal shape with a granular cytoplasm after 4 wk of treatment with specific growth factors and cytokines. Magnification: × 100; B: Uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A (UGT1A) mRNA relative expression quantification. Results were obtained after passage 4 and 9. UGT1A mRNA level in differentiated ADHLSC, were normalized to Cyclophilin A and reported to undifferentiated ADHLSC UGT1A mRNA level; C: In vitro bilirubin conjugation kinetic assessment; Cells were incubated with 100 μmol/L unconjugated bilirubin, supernatants were harvested after 24 h or 48 h. Conjugation rate (CR) was evaluated with high-performance liquid chromatography as follow: [(Conjugated bilirubin concentration)/(Total bilirubin concentration)] x 100. Squares: Wild type hepatocytes (positive control); Triangle: Crigler-Najjar patient hepatocytes (negative control), overturned triangle: undifferentiated ADHLSC, rhomb: differentiated ADHLSC.
- Citation: Maerckx C, Tondreau T, Berardis S, Pelt JV, Najimi M, Sokal E. Human liver stem/progenitor cells decrease serum bilirubin in hyperbilirubinemic Gunn rat. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(30): 10553-10563
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i30/10553.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10553