Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2014; 20(30): 10238-10248
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238
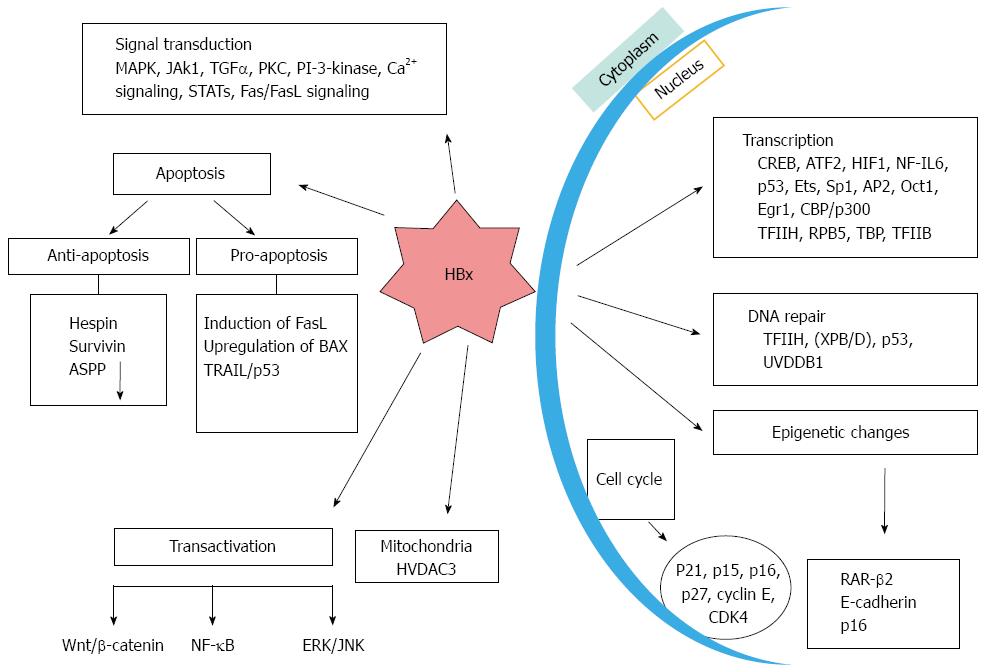
Figure 1 Schematic depicting the potential contributions of hepatitis B virus -encoded protein in different cellular processes.
It influences the apoptosis, transcription, DNA repair and epigenetic changes as well as affecting transactivation mechanism. MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; TGF: Transforming growth factor; IL: Interleukin; PKC: Protein kinase C; ATF: Activating transcription factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; ASPP: Apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinases; JNK: Janus kinase; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor.
- Citation: Ali A, Abdel-Hafiz H, Suhail M, Al-Mars A, Zakaria MK, Fatima K, Ahmad S, Azhar E, Chaudhary A, Qadri I. Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(30): 10238-10248
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i30/10238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238