Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2014; 20(3): 774-785
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.774
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.774
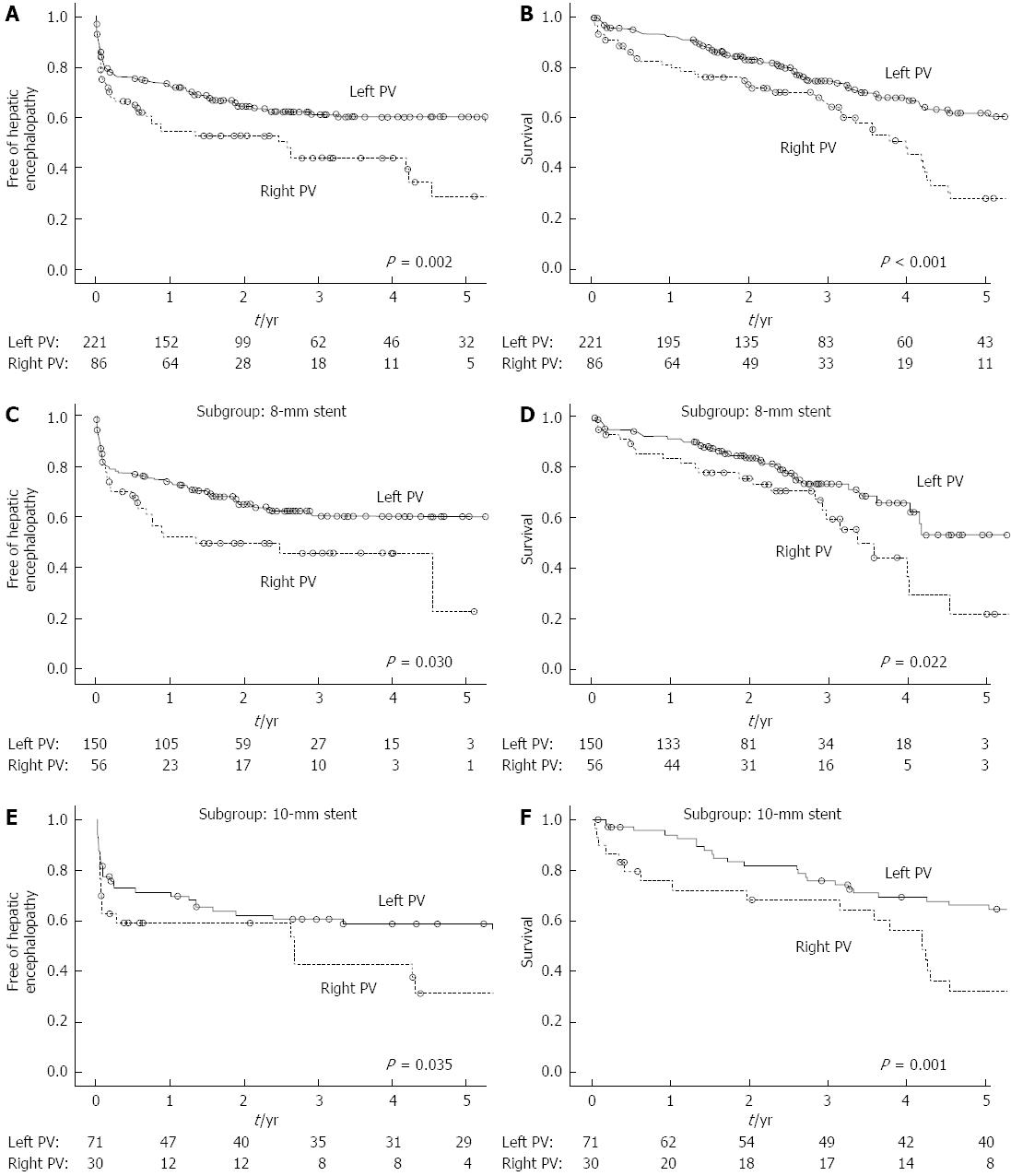
Figure 3 Hepatic encephalopathy results from the Kaplan-Meier analyses.
Comparison of hepatic encephalopathy between the patients with a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) to the left portal vein (PV) and those with a TIPS to the right PV in all patients (A), an 8-mm stent subgroup (C) and a 10-mm stent subgroup (E). Comparisons of survival between the patients with a TIPS to the left PV and those with a TIPS to the right PV in all patients (B), an 8-mm stent subgroup (D) and a 10-mm stent subgroup (F).
- Citation: Bai M, He CY, Qi XS, Yin ZX, Wang JH, Guo WG, Niu J, Xia JL, Zhang ZL, Larson AC, Wu KC, Fan DM, Han GH. Shunting branch of portal vein and stent position predict survival after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(3): 774-785
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i3/774.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.774