Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2014; 20(3): 755-773
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.755
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.755
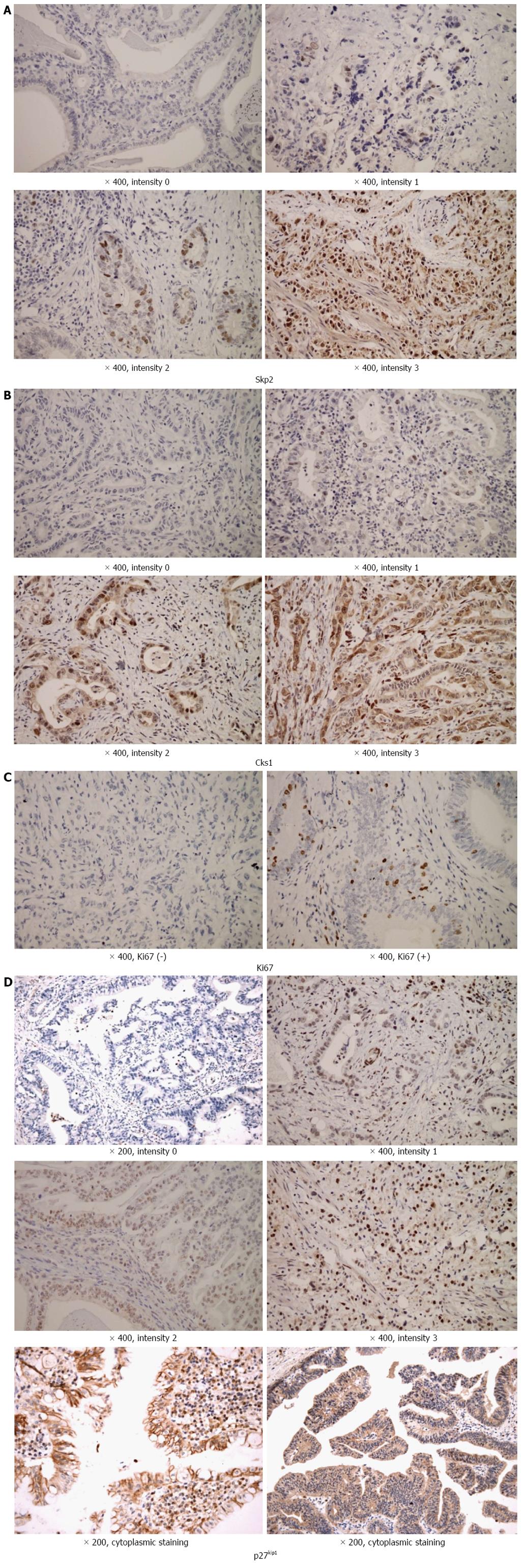
Figure 1 Results of immunohistochemical staining.
A-C: Immunohistochemistry for (A) Skp2, (B) Cks1, and (C) Ki67 proteins showed that stains were mainly expressed in the nuclei of cancer cells; D: The staining pattern of p27kip1 was somewhat heterogeneous. The pattern of nuclear staining was mainly noticed, and some of them were expressed as diffuse cytoplasmic staining. The staining intensity of Skp2, Cks1, and p27kip1 was classified as follows: 0, no staining; 1, weak; 2, moderate; 3, strong. The staining pattern of Ki-67 was nuclear and classified as positive or negative. At least 20 high-power fields will be randomly chosen, and 2000 cells will be always counted. Skp2: S-phase kinase-associated protein 2; Cks1: Cyclin-dependent kinases regulatory subunit 1.
- Citation: Kim JY, Kim HJ, Park JH, Park DI, Cho YK, Sohn CI, Jeon WK, Kim BI, Kim DH, Chae SW, Sohn JH. Epidermal growth factor upregulates Skp2/Cks1 and p27kip1 in human extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(3): 755-773
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i3/755.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.755