Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2014; 20(3): 630-638
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.630
Published online Jan 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.630
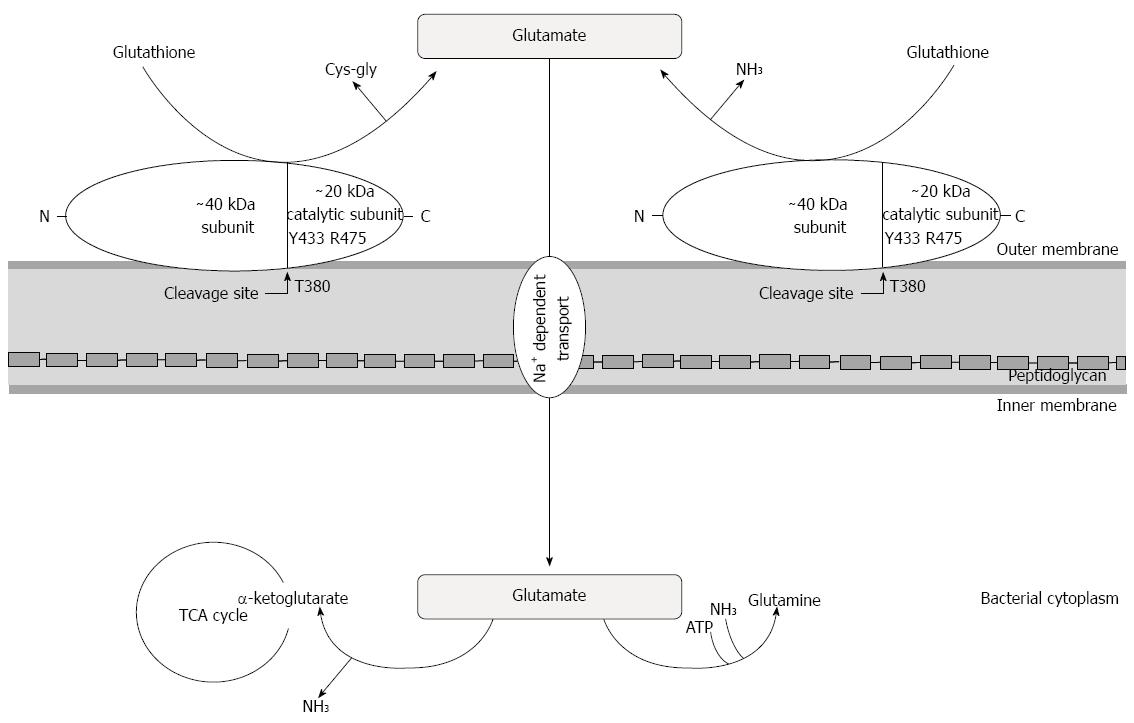
Figure 1 Biochemical features and physiological role of Helicobacter pylori gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) is a secreted protein of 40 and 20 kDs subunits that converts glutamine to glutamate and ammonia, and glutathione to glutamate and cysteinylglycine. The glutamate produced is then transported into H. pylori cells, where it is incorporated into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or utilized for glutamine synthesis.
-
Citation: Ricci V, Giannouli M, Romano M, Zarrilli R.
Helicobacter pylori gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and its pathogenic role. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(3): 630-638 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i3/630.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.630