Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 10094-10107
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10094
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10094
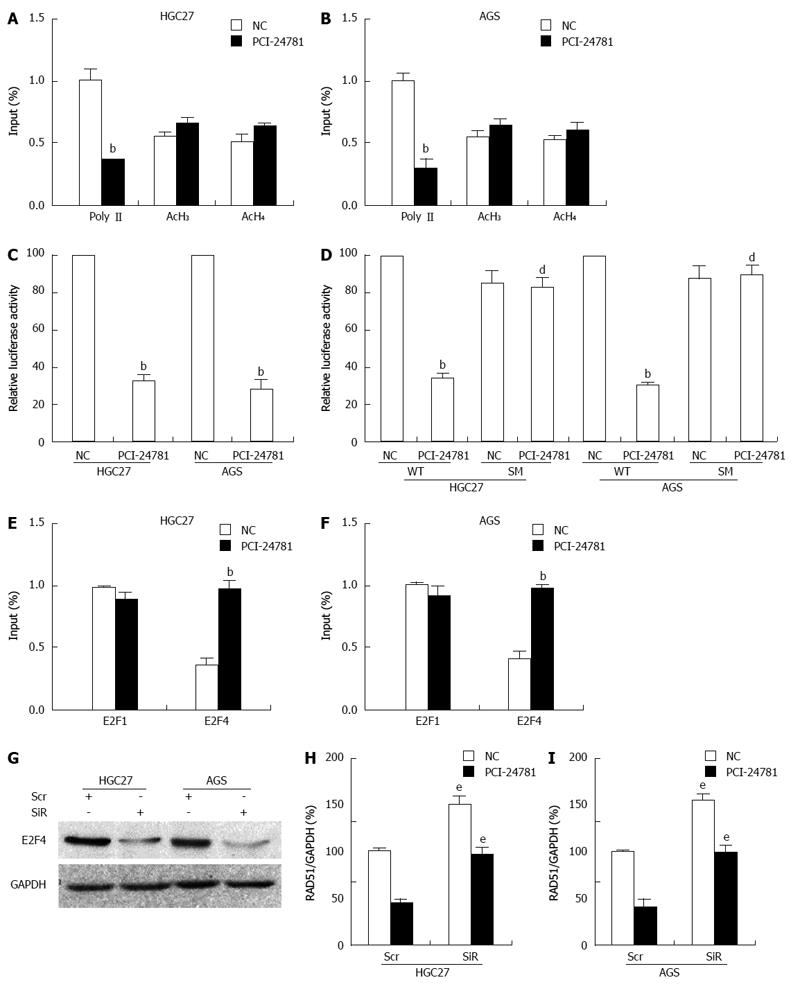
Figure 5 PCI-24781 induces RAD51 transcriptional repression.
A, B: Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed a decrease in Polymerase II binding to the transcribed region of the proximal RAD51 gene in gastric cancer (GC) cells in response to treatment with 0.5 μmol/L PCI-24781 for 24 h; binding of acetylated histones 3 and 4 to the RAD51 region was slightly enhanced. No significant nonspecific IgG binding was observed, and input DNA was used as a loading control; C: Luciferase assays demonstrated that treatment with 0.5 μmol/L PCI-24781 for 24 h resulted in the suppression of RAD51 promoter activity; D: Mutation of the E2F binding site located within the first 50 bp of the RAD51 promoter construct abrogated the aforementioned repression; E, F: ChIP analysis showed significantly enhanced E2F4 binding and slightly decreased E2F1 binding to the cis element in the RAD51 promoter in response to PCI-24781 treatment (0.5 μmol/L for 24 h); G: siRNA targeting E2F4 dramatically decreased the expression of E2F4; H, I: Depletion of E2F4 significantly increased the expression of RAD51 and reversed the PCI-24781-induced decrease in RAD51 expression. SM: E2F binding-site mutation; Scr: Scramble siRNA; SiR: siRNA-E2F4. bP < 0.01 vs the control; dP < 0.01 vs wild-type (WT); eP < 0.05 vs Scr.
-
Citation: He WL, Li YH, Hou WJ, Ke ZF, Chen XL, Lu LY, Cai SR, Song W, Zhang CH, He YL. RAD51 potentiates synergistic effects of chemotherapy with PCI-24781 and
cis -diamminedichloroplatinum on gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 10094-10107 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/10094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10094