Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 10082-10093
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10082
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10082
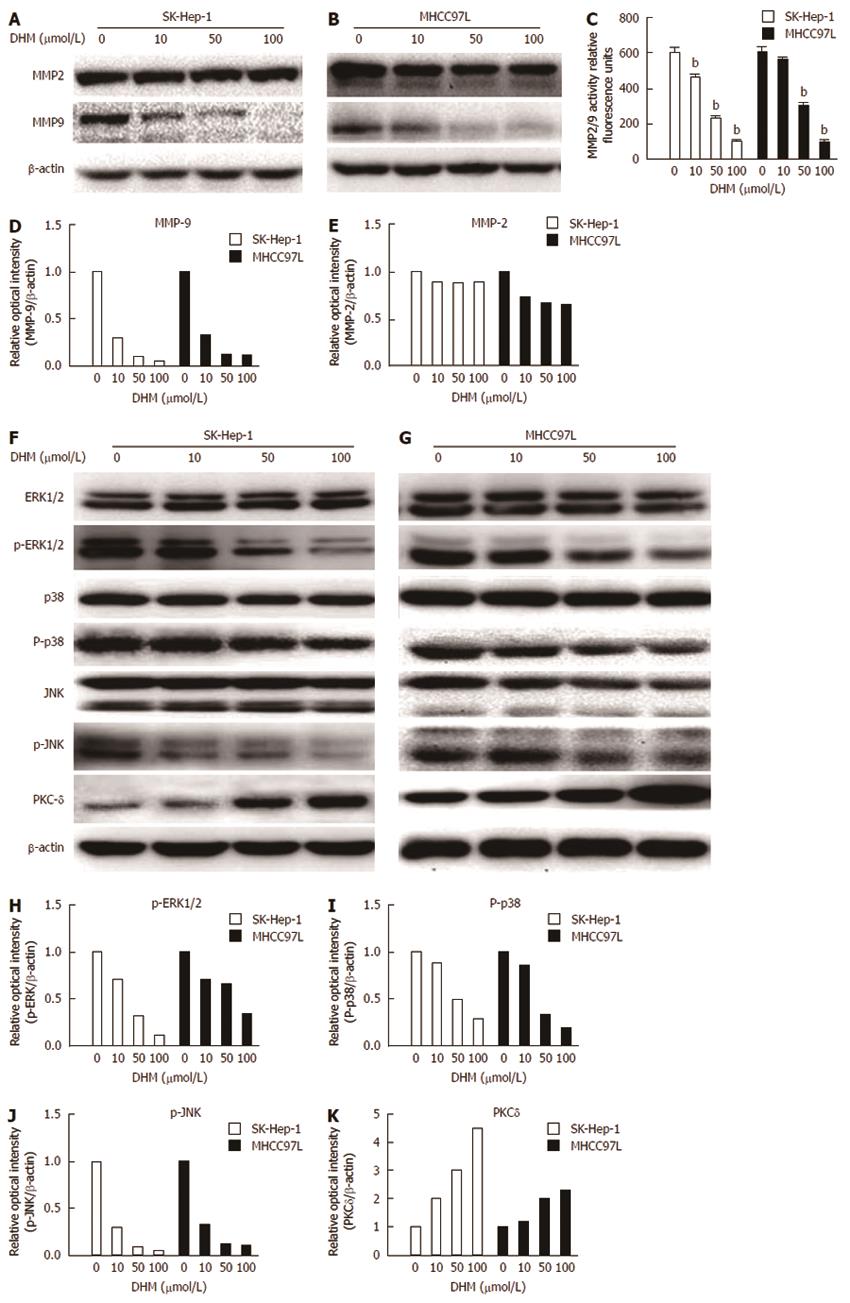
Figure 5 Effect of dihydromyricetin on matrix metalloproteinase-2/matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and the signaling pathways upstream of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9.
SK-Hep-1 and MHCC97L cells were treated with or without dihydromyricetin at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. The cells were then collected and lysed in lysis buffer. The total cell lysates were examined by Western blot. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 protein expression was detected by Western blot in SK-Hep-1 (A, D) and MHCC97 L (B, E) cells after dihydromyricetin (DHM) treatment for 24 h. MMP2/9 activity was measured by fluorescence analysis (C). The levels of ERK1/2, p38, JNK, PKC-δ, p-ERK1/2, p-p38, and p-JNK in SK-Hep-1 (F) and MHCC97L (G) cells were also measured by Western blot assays. A bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay was used to measure the protein concentration of each sample. DHM regulated p-ERK1/2 (H), P-p38 (I), p-JNK (J) and PKC-δ (K) levels in a concentration-dependent manner. bP < 0.01 vs control, Student’s t test.
- Citation: Zhang QY, Li R, Zeng GF, Liu B, Liu J, Shu Y, Liu ZK, Qiu ZD, Wang DJ, Miao HL, Li MY, Zhu RZ. Dihydromyricetin inhibits migration and invasion of hepatoma cells through regulation of MMP-9 expression. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 10082-10093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/10082.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10082